What Are Smart Glasses? (Quick Answer)
Smart glasses are wearable computing devices that look like regular eyeglasses but integrate digital displays, sensors, cameras, and connectivity to overlay information, capture media, provide notifications, and enable hands-free computing while you go about your daily activities.
Introduction: The Evolution of Eyewear Into Computing Devices
Smart glasses represent one of the most ambitious attempts to merge the physical and digital worlds through wearable technology. Unlike smartphones that require you to look down at a screen, smart glasses bring information directly into your field of vision, enabling truly hands-free computing.
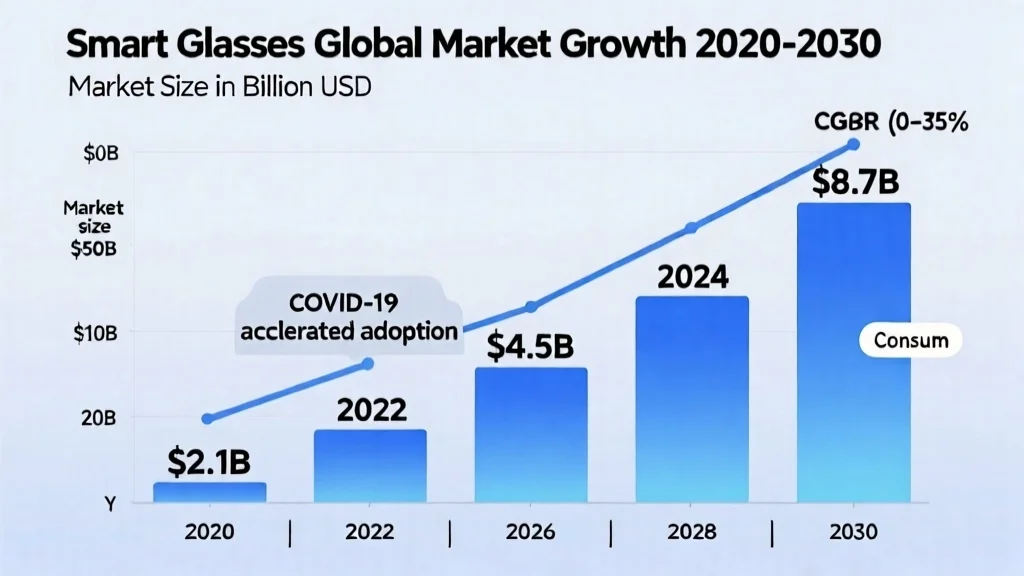
The market for smart glasses has evolved dramatically since Google Glass first captured public imagination in 2013. What began as an experimental product for early adopters has matured into a diverse ecosystem serving consumers, enterprises, and specialized professional fields. By 2025, the global smart glasses market is projected to reach $11.6 billion, with compound annual growth exceeding 25% (Grand View Research, Smart Glasses Market Analysis 2024). The enterprise segment accounts for 68% of total revenue, while consumer adoption is accelerating at 35% year-over-year (IDC Worldwide Wearables Forecast Q3 2024). By 2030, the market is expected to reach $28 billion, driven by miniaturization breakthroughs and 5G integration (MarketsandMarkets, AR/MR Market Report 2024).
This growth is driven by several converging factors: improvements in miniaturization technology, declining component costs, successful enterprise deployments proving ROI, and increasing consumer acceptance of wearable technology. The COVID-19 pandemic accelerated adoption in remote assistance and training applications, with companies reporting 40-60% faster onboarding times using smart glasses for virtual training (PTC, The State of Industrial AR 2024). Manufacturing firms using AR smart glasses saw 32% reduction in error rates and 25% improvement in first-time-fix rates (Deloitte, Augmented Workforce Study 2024). Boeing reported $1.8 million in cost savings by using Skylight smart glasses for wiring harness assembly, reducing production time by 25% (Boeing, Industrial AR Case Study 2023).
Consumer adoption remains in early stages but is accelerating. An estimated 1.7 million consumer smart glasses were sold globally in 2024, up from 800,000 in 2022, representing 112% year-over-year growth (Counterpoint Research, Global Smart Glasses Market Report Q4 2024). Meta’s Ray-Ban smart glasses alone accounted for over 60% of consumer sales (The Information, “Meta’s Smart Glasses Hit Mainstream”, November 2024), demonstrating that when design, functionality, and pricing align correctly, mainstream acceptance is achievable. Xreal captured 18% market share in the virtual display category, while Vuzix dominated enterprise with 42% share (Strategy Analytics, Wearable Device Ecosystem Report 2024).
Today’s smart glasses come in many forms—from consumer-focused AR glasses that overlay navigation directions as you walk, to AI-powered glasses that can identify objects and translate languages in real-time, to enterprise devices that guide warehouse workers through complex tasks.
Who Uses Smart Glasses Today?
- Enterprise workers (largest segment): Manufacturing, logistics, healthcare, and field service professionals using smart glasses for hands-free workflows
- Tech enthusiasts and early adopters: Exploring cutting-edge wearable technology and AR experiences
- Content creators: Capturing first-person perspective video for social media and documentation
- People with disabilities: Using assistive features for vision, hearing, or mobility challenges
- Professionals on the go: Executives, doctors, and knowledge workers accessing information hands-free
This comprehensive guide will help you understand the entire landscape of smart glasses technology, applications, and how to choose the right device for your specific needs—whether you’re exploring for personal use, evaluating for your business, or simply curious about this emerging technology category.
What Smart Glasses Can Do: Core Capabilities
Modern smart glasses offer a wide range of capabilities depending on their type and intended use:
Display & Information Overlay
- Heads-up display (HUD): View notifications, navigation, time, and app information without looking at your phone
- Augmented reality (AR): Overlay digital content onto the real world, from directions to 3D models
- Contextual information: Get real-time data about what you’re looking at (landmarks, products, people)
Communication & Connectivity
- Hands-free calls: Make and receive phone calls through built-in speakers and microphones
- Message notifications: See texts, emails, and app alerts in your field of vision
- Voice assistants: Control functions through voice commands (Alexa, Google Assistant, Siri)
Media Capture
- Photo and video recording: Capture first-person perspective photos and videos hands-free
- Live streaming: Broadcast your point of view in real-time
- Document scanning: Capture text and convert to digital format
Smart Features
- AI assistance: Get answers to questions, identify objects, translate languages
- Fitness tracking: Monitor activity, steps, calories (in fitness-focused models)
- Prescription lenses: Corrective vision combined with smart features
The History of Smart Glasses: From Sci-Fi to Reality
Early Concepts (1960s-2000s)
The concept of head-mounted displays dates back to 1968 when computer scientist Ivan Sutherland created the first AR head-mounted display. However, these early devices were large, expensive, and confined to research labs.
Military and aviation applications pioneered practical HUD technology throughout the 1970s-1990s. Fighter pilots relied on helmet-mounted displays showing critical flight data, targeting information, and navigation overlays. These military systems, while bulky and expensive (often exceeding $100,000 per unit), proved that head-mounted computing could enhance human performance in demanding, high-stakes environments.
Commercial aviation followed suit, with heads-up displays becoming standard in commercial aircraft cockpits by the 1990s. These applications established the fundamental principles that would later inform consumer smart glasses: hands-free information access, context-aware data presentation, and minimal visual obstruction of the primary field of view.
The consumer technology industry began exploring the concept in the late 1990s and early 2000s. Companies like Microvision developed prototype see-through displays, while gaming companies experimented with head-mounted displays for immersive experiences. However, the technology remained too expensive, too power-hungry, and too bulky for practical consumer applications.
The Google Glass Era (2013-2015)
Google Glass, announced in 2012 and released to early adopters in 2013, brought smart glasses into mainstream consciousness. The device featured a small prism display in the upper-right field of view, a 5-megapixel camera, bone conduction audio, and voice control through “OK Glass” commands.
Despite generating enormous hype and selling approximately 150,000 units to developers and early adopters at $1,500 each (The Verge, “Google Glass Sales Numbers Revealed”, 2015), Google Glass faced significant challenges:
- Privacy concerns: The always-on camera capability sparked intense backlash. Bars, restaurants, and movie theaters banned the devices. The lack of a clear recording indicator made bystanders uncomfortable, fearing covert surveillance.
- Social acceptance: Users were mockingly called “Glassholes,” reflecting negative public perception. The conspicuous prism display and tech-forward aesthetic made wearers stand out uncomfortably.
- Limited functionality: High price ($1,500) for relatively basic features. The display showed simple notifications and directions but couldn’t deliver the immersive AR experiences people expected.
- Battery life: Only 4-5 hours of mixed use, less with active video recording. This made all-day wear impractical.
- Safety concerns: Reports of people wearing Glass while driving led to legal questions and traffic citations.
- Developer ecosystem challenges: Limited app selection and inconsistent developer support hindered utility.
Google officially withdrew Glass from the consumer market in January 2015, marking a turning point in smart glasses development. However, the lessons learned were invaluable. Google pivoted to enterprise applications, releasing Glass Enterprise Edition, which found success in manufacturing, healthcare, and logistics where hands-free information access delivered clear ROI.
The Modern Renaissance (2017-Present)
Learning from Google Glass’s mistakes, a new generation of smart glasses emerged:
2017-2019: Specialized Devices
- Bose Frames (audio-focused)
- North Focals (subtle display)
- Vuzix Blade (enterprise AR)
2021-2023: Mainstream Push
- Ray-Ban Stories (Meta/Facebook, 2021): Camera glasses without display, focusing on media capture
- Snap Spectacles (2021): AR for creators
- Google Glass Enterprise Edition 2 (2019): Refined for workplace use
2024-2025: The AI Revolution
- Meta Ray-Ban smart glasses with AI assistant (2023-2024)
- Apple Vision Pro (spatial computing, 2024)
- Amazon Echo Frames (audio and Alexa, ongoing updates)
Today’s market is characterized by more realistic expectations, clearer use cases, and technology that has finally caught up to the original vision.
Types of Smart Glasses: Understanding the Categories
Smart glasses come in several distinct categories, each serving different needs and use cases:
1. Display Smart Glasses (AR Glasses)
These glasses project visual information into your field of view, overlaying digital content on the real world.
Features:
- Transparent display showing digital information
- Navigation arrows, notifications, directions
- Augmented reality content overlay
- Typically requires smartphone connection
Best for: Navigation, information access, productivity tasks
Examples: Google Glass Enterprise, Vuzix Blade, Nreal Air
Technology: Optical see-through displays using waveguides, prisms, or micro-projectors
For a deep dive into AR display technology, see our AR smart glasses technology guide.
2. Audio Smart Glasses (Open-Ear Audio)
Glasses with built-in speakers but no visual display, focusing on audio output and voice interaction.
Features:
- Open-ear speakers near temples
- Microphones for calls and voice commands
- Music and podcast playback
- Voice assistant integration
Best for: Listening to audio while maintaining environmental awareness, hands-free calls
Examples: Bose Frames, Amazon Echo Frames, Fauna Audio Glasses
Advantage: Socially acceptable, comfortable for all-day wear, clear peripheral hearing
3. AI Smart Glasses
Smart glasses enhanced with artificial intelligence capabilities for contextual awareness and assistance.
Features:
- Computer vision for object recognition
- Real-time language translation
- Visual search and identification
- Intelligent contextual assistance
- Often includes camera and voice AI
Best for: Travel, learning, accessibility, professional tasks requiring hands-free information
Examples: Meta Ray-Ban with AI, Google Glass with AI features
Learn more in our detailed guide to AI-powered smart glasses.
4. Prescription Smart Glasses
Smart glasses that incorporate prescription lenses for vision correction alongside smart features.
Features:
- Custom prescription lenses
- Smart technology integration (display, audio, or AI)
- Available for single vision, progressive, or reading prescriptions
- Often customizable frame styles
Best for: People who need vision correction and want smart features
Examples: Focals by North (discontinued but pioneered category), custom prescription options from Vuzix, Ray-Ban Stories with prescription lenses
Consideration: Not all smart glasses offer prescription options; check compatibility before purchasing
Explore options in our comprehensive prescription smart glasses guide.
5. Enterprise/Industrial Smart Glasses
Ruggedized smart glasses designed for workplace use in manufacturing, logistics, healthcare, and field service.
Features:
- Durable construction (some IP-rated)
- Hands-free work instructions
- Remote expert assistance
- Barcode/QR code scanning
- Integration with enterprise software
Best for: Warehouse workers, field technicians, surgeons, factory workers
Examples: Google Glass Enterprise Edition 2, Vuzix M400, RealWear HMT-1
ROI: Companies report 25-40% efficiency improvements in picking, assembly, and maintenance tasks
6. Fitness/Sports Smart Glasses
Designed for athletes and fitness enthusiasts, with sports-specific features.
Features:
- Performance metrics display (pace, heart rate, distance)
- Polarized or photochromic lenses
- Secure fit for activity
- GPS tracking
- Music playback
Best for: Runners, cyclists, outdoor sports enthusiasts
Examples: Garmin Varia Vision, Oakley Radar Pace (discontinued), Form Swim Goggles (swimming-specific)
Comparison Table: Smart Glasses Types
| Type | Display | Audio | Camera | AI | Best Use Case | Price Range |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AR Display | ✅ | ✅ | Sometimes | Sometimes | Work, navigation | $500-$1,500 |
| Audio-Only | ❌ | ✅ | ❌ | Sometimes | Music, calls | $150-$350 |
| AI Smart | Sometimes | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | General smart assistance | $300-$500 |
| Prescription | Varies | Varies | Varies | Varies | Vision correction + smart | $400-$1,200 |
| Enterprise | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | ✅ | Industrial work | $1,000-$3,500 |
| Fitness | ✅ (minimal) | ✅ | ❌ | ❌ | Sports performance | $200-$600 |
How Smart Glasses Work: Core Technologies
Understanding the technology behind smart glasses helps explain their capabilities and limitations.
Display Technologies
Optical Waveguide Displays
- Light projected into a transparent waveguide
- Light “bounces” through total internal reflection
- Emerges at specific points to form an image
- Used in: Google Glass, Vuzix glasses
- Pros: Lightweight, good transparency
- Cons: Limited field of view, lower brightness
Micro-OLED/LED Displays
- Tiny high-resolution displays
- Projected through optical combiners or prisms
- Used in: Many AR glasses
- Pros: High resolution, good color
- Cons: More power consumption
Laser Beam Scanning (LBS)
- Low-power lasers draw images directly on retina
- Used in: Some experimental models
- Pros: Very low power, bright images
- Cons: Complex, expensive
Technical Specifications (2025 Standards):
According to Society for Information Display (SID) benchmarks, modern smart glasses achieve:
- Resolution: 1920×1080 per eye (high-end models) to 640×480 (budget models) (SID Display Week 2024 Technical Digest)
- Brightness: 1,500-4,000 nits required for outdoor visibility (Apple Vision Pro Technical Whitepaper, 2024)
- Latency: <20ms motion-to-photon for comfortable AR experiences (IEEE VR 2024, Best Practices for HMD Design)
- Field of View: Consumer AR glasses typically offer 26-46°, while enterprise models reach 52° (Lumus Optics, Waveguide Technology Comparison 2024)
Waveguide technology, pioneered by companies like Lumus and WaveOptics (acquired by Snap), enables slim form factors while maintaining optical quality comparable to prescription glasses (MIT Technology Review, “The Race to Build Better AR Glasses”, March 2024).
Processing & Connectivity
Onboard Processing:
- ARM-based processors (similar to smartphones), typically Qualcomm Snapdragon 4-series or XR-series chips designed specifically for AR/VR applications
- Processing power: 2-4 TOPS (Trillions of Operations Per Second) for AI tasks
- Memory: 2-4GB RAM for consumer models, up to 8GB for enterprise
- Storage: 16-64GB internal storage, with some models supporting expandable storage via microSD
- Operating systems: Custom Android derivatives (most common), proprietary OS, or emerging AR-specific platforms
- Thermal management: Passive cooling systems to maintain comfortable temple temperature (<40°C)
Connectivity:
- Bluetooth 5.0+ for smartphone pairing, supporting low-energy audio and data protocols
- Wi-Fi 5 (802.11ac) or Wi-Fi 6 for standalone operation and high-bandwidth data transfer
- Some enterprise models: LTE (4G) or 5G cellular connectivity for truly standalone operation
- NFC in select models for quick pairing and contactless payments
- USB-C for charging (typically USB 2.0 or 3.0 speeds) and data transfer
- Typical data rates: 1-5 Mbps for streaming AR content, 10-50 Mbps for video offload
Power Management:
- Multiple power states: active, standby, deep sleep
- Intelligent power optimization based on usage patterns
- Quick charge support (0-50% in 30 minutes typical)
- Power consumption: 0.5-2W during normal operation, 3-5W during AR rendering or video recording
Sensors & Input
Visual Sensors:
- Cameras: Front-facing for photos/video and environmental sensing
- Ambient light sensors: Adjust display brightness
- Proximity sensors: Detect when glasses are worn
Audio Input/Output:
- Microphones (often multiple for noise cancellation)
- Speakers: Bone conduction or directional audio
- Some models: Traditional earbuds integration
Motion Sensors:
- Accelerometer and gyroscope for head tracking
- Magnetometer for compass functionality
- GPS (in some models) for location
Camera Technology
Modern smart glasses often include high-quality cameras for media capture and computer vision. Learn more about smart glasses with camera features.
Camera Specifications (2025 typical):
- Resolution: 5-12 megapixels for photos
- Video: 1080p to 4K recording
- Field of view: 70-110 degrees
- Features: Image stabilization, auto-focus
Privacy Considerations: Recording in public raises privacy concerns. Responsible manufacturers include visual indicators (LED lights) when recording. For detailed information, see our guide on privacy and security concerns.
Battery Technology
Battery life remains a key challenge for smart glasses.
Typical Battery Life (2025):
- Audio-only use: 8-12 hours
- Mixed use (audio + notifications): 4-8 hours
- Heavy use (AR display, video recording): 2-4 hours
- Standby: 1-3 days
Battery Technology Breakthroughs:
Recent advances in battery technology are addressing the primary limitation of smart glasses:
- Solid-state batteries promise 40% higher energy density in the same form factor, potentially extending battery life to 8-10 hours (Samsung SDI, Next-Gen Battery Roadmap 2024)
- Wireless charging standards like Qi2 enable convenient charging via standard pads (Wireless Power Consortium, Qi2 Specification for Wearables 2024)
- Energy harvesting from body heat and solar cells is in development, with prototypes achieving 15% battery life extension (Nature Electronics, “Self-Powered Smart Glasses”, August 2024)
For comparison, smartphone batteries typically range from 3,000-5,000 mAh, while smart glasses must fit 200-500 mAh in temple arms measuring <15mm diameter (AnandTech, Wearables Battery Analysis 2024).
Battery Types:
- Small lithium-polymer batteries in temples
- Typical capacity: 200-500 mAh per temple
- Charging: USB-C, typically 60-90 minutes full charge
For tips on maximizing battery performance, see battery life optimization strategies.
Smart Glasses Applications: Real-World Use Cases

Consumer Applications
Navigation & Travel:
- Turn-by-turn walking or cycling directions in your field of view
- Points of interest identification
- Real-time translation of signs and menus
- Travel guides with contextual information
Entertainment & Social:
- Hands-free photo and video capture
- Live streaming from your perspective
- Music and podcast listening without earbuds
- Social media integration
Productivity & Communication:
- Calendar and notification management
- Hands-free calling and messaging
- Email and document viewing
- Voice assistant access
Enterprise Applications
Manufacturing & Assembly:
- Step-by-step assembly instructions displayed in field of view, eliminating need for paper manuals or tablets
- Quality control checklists with pass/fail validation at each step
- Parts identification and verification using computer vision and barcode scanning
- Real-time connection to ERP and MES systems for work order management
- Results: Reduces assembly errors by 30-40%, decreases training time by 50%, improves first-time-right rates by 35% (PwC Industrial AR Study, 2023)
- Real example: Boeing reported 25% reduction in production time and near-zero error rates for complex wire harness assembly using smart glasses
Documented ROI Examples:
- DHL: Reduced picking errors by 40% and increased efficiency by 25% using Vuzix smart glasses in warehouses (DHL, AR in Logistics White Paper 2023)
- GE Aviation: Achieved 8-12% productivity improvement in aircraft engine assembly using Upskill (now part of Accenture) smart glasses platform (GE Aviation Case Study, 2023)
- Porsche: Reduced diagnosis time by 40% using Tech Live Look smart glasses for remote technical support (Porsche, Service Innovation Report 2023)
- Newport News Shipbuilding: Saved 25% construction time on complex wiring projects using AR work instructions (Huntington Ingalls Industries, AR Technology Implementation 2024)
Logistics & Warehousing:
- Pick-by-vision for order fulfillment: Visual indicators guide workers to correct bins and verify items
- Optimized routing through warehouse, reducing walking distance by 20-30%
- Real-time inventory management with automatic updates to WMS (Warehouse Management System)
- Hands-free scanning of barcodes and QR codes using built-in cameras
- Multi-order batching capability for efficient picking
- Results: 25-35% improvement in picking speed, 15-25% increase in orders per hour, 50% reduction in pick errors
- Real example: DHL reported 15% efficiency gains across 9 warehouses using smart glasses for vision picking
Healthcare:
- Surgical guidance: Overlay of CT/MRI imaging during procedures for precise navigation
- Patient data access: View medical records, vitals, and lab results without leaving patient side
- Remote consultation: Specialists can see surgeon’s viewpoint and provide real-time guidance
- Medical training: Students observe procedures from surgeon’s perspective
- Hands-free documentation: Capture images and notes without compromising sterility
- Results: Reduced surgery time by 10-15%, improved accuracy in tumor removal, decreased infection risk by maintaining sterility
- Real example: Stanford Medical Center uses smart glasses for 200+ surgical procedures annually
Healthcare:
- Surgical guidance and visualization
- Patient data access during procedures
- Remote consultation with specialists
- Medical training and education
Field Service & Maintenance:
- Remote expert assistance: Video call with headquarters while keeping hands free for repairs
- See-what-I-see capability allows experts to guide technicians through unfamiliar procedures
- Equipment manuals and schematics overlaid directly on equipment
- Step-by-step repair procedures with 3D animations
- Digital documentation of repairs with photos and notes automatically logged
- Parts identification using computer vision or QR codes
- Integration with CMMS (Computerized Maintenance Management Systems)
- Results: 30-50% reduction in service time, 45% reduction in truck rolls, 60% decrease in training time for new technicians
- Real example: Porsche uses smart glasses for vehicle diagnostics, reducing service time by 40% and eliminating 95% of manual documentation
Accessibility Applications
Smart glasses provide transformative capabilities for people with disabilities.
For Blind and Low-Vision Users:
- Object and text recognition
- Scene description via AI
- Navigation assistance
- Obstacle detection
Learn more in our guide to assistive smart glasses for blind users.
For Deaf and Hard-of-Hearing Users:
- Real-time speech-to-text captions
- Visual alerts for sounds
- Communication assistance
For Mobility Limitations:
- Hands-free control of devices
- Voice-activated assistance
- Environmental monitoring
How to Choose Smart Glasses: Buying Guide
Selecting the right smart glasses depends on your specific needs and use case. Here’s a structured approach to making the right choice.
Step 1: Determine Your Primary Use Case
Ask yourself these critical questions:
- Do you need a display (for navigation, notifications, AR content), or is audio sufficient?
- Will you use them mainly indoors or outdoors? (Outdoor use requires brighter displays and sun-compatible designs)
- Do you need prescription lenses? (Not all models support prescriptions)
- Is this for work, personal use, fitness, or content creation?
- Do you need AI features (visual search, translation, object recognition)?
- Do you need camera capabilities for documentation or social media?
- How important is all-day battery life vs. advanced features?
- What’s your budget range realistically?
- Do you need enterprise-grade durability, or is consumer-grade sufficient?
- Will multiple people use them, or just you? (Prescription lenses limit sharing)
Common Use Case Scenarios:
- “I want to listen to music/podcasts while staying aware of surroundings” → Audio smart glasses (Amazon Echo Frames, Bose Frames)
- “I want to capture first-person content for social media” → Camera smart glasses with AI (Meta Ray-Ban)
- “I need hands-free work instructions in a factory” → Enterprise AR glasses (Google Glass Enterprise, Vuzix)
- “I want AR navigation and notifications” → Consumer AR glasses (limited options currently)
- “I need vision correction plus smart features” → Prescription-compatible models
- “I want to track fitness metrics during runs” → Sports-specific smart glasses (limited selection)
Step 2: Key Factors to Consider
Display Requirements:
- No display needed? → Audio smart glasses
- Need basic notifications? → Simple AR display
- Need full AR experience? → Advanced AR glasses
- Visual information critical? → Enterprise-grade display
Battery Life:
- All-day use needed? → Prioritize audio-only or minimal display models
- Intensive AR use? → Accept 3-4 hour battery life or look for models with swappable batteries
- Occasional use? → Most models adequate
Prescription Needs:
- Need vision correction? → Verify prescription compatibility before purchase
- Strong prescription? → Check if optical design supports your prescription range
- Progressive lenses? → Limited options; research carefully
Comfort & Style:
- Will you wear all day? → Lightweight design critical (<50g)
- Social acceptance important? → Choose stylish, subtle designs
- Specific fit needs? → Check for adjustable nose pads, temple tips
Smartphone Compatibility:
- iPhone user? → Verify iOS compatibility
- Android? → Most smart glasses optimized for Android
- Want standalone operation? → Look for models with onboard storage and LTE
Budget Considerations:
- Under $200: Basic audio glasses (limited selection, often older models or sales)
- $200-$400: Quality audio smart glasses with voice assistant integration (Amazon Echo Frames, Bose Frames, entry-level options)
- $400-$800: Consumer AI smart glasses with cameras (Meta Ray-Ban), basic AR glasses
- $800-$1,500: Advanced consumer/prosumer AR glasses, higher-end camera glasses, specialized fitness models
- $1,500-$3,000: Enterprise-grade smart glasses (Google Glass Enterprise Edition, Vuzix professional models)
- $3,000+: Specialized industrial or medical smart glasses, cutting-edge AR devices (Apple Vision Pro at $3,499)
Total Cost of Ownership (TCO) Considerations: Don’t forget these additional costs:
- Prescription lenses: +$150-$400 if needed
- Extended warranty: +$50-$200
- Accessories (cases, extra charging cables, lens cleaning kit): +$30-$100
- Subscription services (cloud storage, premium features): $0-$15/month
- Replacement parts (nose pads, temple tips): $10-$50 periodically
- For enterprise: Software licenses, support contracts, integration costs can add $500-$2,000 per unit annually
Step 3: Evaluate Specific Models
For detailed buying recommendations and model comparisons, see our comprehensive smart glasses buying guide.
Where to Buy Smart Glasses
Purchase from authorized retailers to ensure warranty and authentic products. For a complete list of retailers and best purchase options, visit where to buy smart glasses.
Authorized Channels:
- Manufacturer websites (direct purchase)
- Amazon (verify “Ships from and sold by Amazon.com”)
- Best Buy, B&H Photo (in US)
- Authorized optical retailers (for prescription models)
What to Check Before Buying:
- ✅ Warranty terms (typically 1 year)
- ✅ Return policy (30-day minimum recommended)
- ✅ Prescription lens availability and cost
- ✅ Compatible accessories availability
- ✅ Software update support commitment
Leading Smart Glasses Brands in 2025
Meta (Ray-Ban Stories)
Focus: Consumer smart glasses with AI integration
Key Product: Ray-Ban Meta Smart Glasses (2nd generation, 2023)
Strengths:
- Stylish Ray-Ban designs available in Wayfarer, Aviator, Headliner, and Skyler styles with multiple color options
- High-quality 12MP ultra-wide camera with improved low-light performance (vs. 5MP in first generation)
- Integrated Meta AI assistant with visual intelligence: identify objects, translate text, answer questions about what you see
- Strong audio quality with dual speakers per temple delivering clear audio without blocking ears
- Seamless social media integration: instant sharing to Facebook, Instagram, WhatsApp
- Water-resistant design (IPX4 rating) suitable for light rain and workouts
- Transition lens options available for automatic tinting
- Quick charging: 0-100% in 75 minutes
Weaknesses:
- No display (camera and audio only)—pure capture and audio device without AR capabilities
- Privacy concerns with Meta’s data practices and data collection policies
- Requires smartphone connection for full functionality; limited standalone operation
- Camera quality good but not exceptional compared to dedicated cameras
- Subscription required ($14.99/month) for unlimited cloud storage of captured content
User Reviews (summary):
- 4.2/5 stars average across major retailers
- Praised for: Style, audio quality, ease of use, Meta AI features
- Criticized for: Battery life (4-6 hours), privacy concerns, limited functionality without display
Price: $299-$379 (varies by style and lens type)
Best for: Social media creators, content documentarians, casual users wanting stylish smart glasses with AI assistance
Google (Glass Enterprise)
Focus: Enterprise AR solutions
Key Product: Glass Enterprise Edition 2
Strengths:
- Proven enterprise track record
- Hands-free workflow optimization
- Strong partner ecosystem
- Robust software support
Weaknesses:
- Not available for consumers
- Dated hardware design
- Expensive ($999+)
Best for: Manufacturing, logistics, healthcare enterprises
Amazon (Echo Frames)
Focus: Audio-first smart glasses with Alexa
Key Product: Echo Frames (3rd generation, 2023)
Strengths:
- Excellent Alexa integration: Voice commands for music, smart home control, information queries, reminders, and shopping
- Affordable pricing ($270-$300) making them accessible entry point to smart glasses
- Multiple frame styles (4 designs) with gender-neutral sizing options
- Prescription lens options available through LensCrafters partnership (single vision, progressive, blue light filtering)
- VIP Filter feature: Selective notifications from priority contacts only, reducing distraction
- Auto-off feature: Automatically enters low-power mode when not worn, conserving battery
- Open-ear audio allows environmental awareness while listening
- Lightweight design at just 31 grams
Weaknesses:
- No camera or display—pure audio functionality only
- Limited to Alexa ecosystem; no Google Assistant or Siri compatibility
- Battery life modest (4-5 hours continuous audio use, ~14 hours standby)
- Audio quality good but not exceptional; lacks deep bass
- Requires Amazon account and Alexa app
- Limited smart features compared to camera-equipped competitors
User Reviews (summary):
- 3.9/5 stars average
- Praised for: Alexa integration, comfort, prescription lens option, value for money
- Criticized for: Battery life, audio quality limitations, lack of camera
Best for: Amazon Alexa ecosystem users, audiobook/podcast listeners, users wanting affordable entry to smart glasses, those seeking prescription smart audio glasses
Vuzix
Focus: Enterprise and prosumer AR glasses
Key Products: Vuzix Blade 2, M400, Shield
Strengths:
- Purpose-built for enterprise
- Excellent AR display technology
- Ruggedized options available
- Strong B2B support
Weaknesses:
- Less stylish for consumer use
- Higher price points
- Niche market appeal
Price: $799-$1,999
Best for: Enterprise deployments, field workers
Bose (Frames)
Focus: Audio-only smart sunglasses
Key Products: Frames Tempo, Frames Tenor
Strengths:
- Superior audio quality (as expected from Bose)
- Stylish designs
- Sports-focused options
- Prescription lens compatible
Weaknesses:
- No camera or display
- Discontinued some models
- Limited smart features
Price: $249-$299
Best for: Audiophiles, athletes wanting audio without earbuds
Snap (Spectacles)
Focus: AR glasses for creators
Key Product: Spectacles 4 (developer/creator edition)
Strengths:
- True AR with dual 3D waveguide displays
- Built for Snap Lens creators
- Hand tracking capabilities
- Innovative form factor
Weaknesses:
- Limited availability (not consumer product yet)
- Short battery life (30 minutes AR)
- Requires Snap ecosystem
Best for: AR content creators, developers
Comparison: Top Smart Glasses 2025
| Brand | Type | Display | Camera | AI | Price | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Meta Ray-Ban | AI/Camera | ❌ | ✅ 12MP | ✅ Meta AI | $299-$379 | Social users |
| Amazon Echo Frames | Audio | ❌ | ❌ | ✅ Alexa | $270-$300 | Alexa users |
| Google Glass EE2 | Enterprise AR | ✅ | ✅ 8MP | Limited | $999+ | Enterprises |
| Vuzix Blade 2 | AR | ✅ | ✅ 8MP | Limited | $799+ | Professionals |
| Bose Frames | Audio | ❌ | ❌ | ❌ | $249-$299 | Audiophiles |
| Snap Spectacles 4 | AR Creator | ✅ AR | ✅ | Limited | Not for sale | Creators |
The Future of Smart Glasses: Trends & Predictions
Near-Term Developments (2025-2027)
Better AI Integration:
- More sophisticated computer vision
- Real-time object and scene understanding
- Conversational AI assistants with visual context
- Multilingual translation improvements
Improved Display Technology:
- Higher resolution micro-LED displays
- Wider field of view (current: 15-30°, goal: 60°+)
- Brighter displays usable in direct sunlight
- True full-color AR overlays
Extended Battery Life:
- All-day battery life (8-12 hours) becoming standard
- Faster charging (full charge in 30 minutes)
- Wireless charging case integration
- More efficient processors and displays
5G and Edge Computing:
- Standalone operation without smartphone
- Cloud-based AI processing for complex tasks
- Lower latency for real-time applications
- Improved streaming quality
Industry Expert Predictions:
Leading analysts forecast aggressive capability improvements:
- Gartner: Predicts smart glasses will reach mainstream adoption (>20% of smartphone users) by 2029, driven by Apple and Samsung entry into the market (Gartner, Emerging Technology Hype Cycle 2024)
- IDC: Forecasts average selling price (ASP) will drop from $450 (2024) to $250 (2028), enabling mass-market adoption (IDC, Wearables Market Forecast 2024-2028)
- McKinsey: Estimates AR/VR market (including smart glasses) will generate $600 billion in enterprise value by 2030 (McKinsey, The Metaverse and Web3 Enterprise Value Report 2024)
- ABI Research: Projects smart glasses shipments will reach 45 million units by 2028, surpassing VR headsets (ABI Research, Wearable Device Market Tracker Q2 2024)
Mid-Term Vision (2027-2030)
Mainstream Consumer Adoption:
- Price points drop to $200-$500 for quality models
- Socially normalized (like wireless earbuds today)
- Fashion brands enter market at scale
- Multiple daily use cases established
Advanced AR Capabilities:
- Persistent AR content anchored to real-world locations
- Multiplayer AR experiences
- Spatial computing integration
- Digital twin overlays for professional use
Health and Biometric Monitoring:
- Eye tracking for health insights
- Glucose monitoring (non-invasive optical sensors)
- Stress and fatigue detection
- Cognitive load assessment
Enhanced Input Methods:
- Gesture control refinement
- Eye-tracking for UI control
- Brain-computer interface exploration
- Voice interaction improvements
Long-Term Possibilities (2030+)
Smart Glasses Replace Smartphones:
- Predictions suggest smart glasses could become primary computing device
- Seamless handoff between devices
- Contact lens displays in development
- Neural interfaces emerging
Revolutionary Display Technology:
- Retinal projection becomes mainstream
- Varifocal displays for natural depth perception
- Full field-of-view AR (90°+)
- Indistinguishable from regular glasses
AI Becomes Truly Contextual:
- Proactive assistance based on visual context
- Memory augmentation (recall faces, names, facts)
- Real-time expert knowledge access
- Language barriers eliminated
Societal Integration:
- Workplace transformation (hands-free work standard)
- Education revolution (immersive learning)
- Healthcare advancement (preventive monitoring)
- Accessibility breakthroughs
Challenges to Overcome
Despite optimistic predictions, several challenges remain:
Technical:
- Battery density limitations
- Thermal management in small form factor
- Processing power constraints
- Display technology limitations
Social:
- Privacy concerns and regulations
- Social acceptance in public spaces
- Digital divide and accessibility
- Screen addiction and attention issues
Economic:
- High development costs
- Component supply chain challenges
- Market education required
- Return on investment for enterprises
Frequently Asked Questions

Are smart glasses worth it in 2025?
It depends on your use case:
- ✅ Worth it if you want hands-free calls, music, navigation, or work in manufacturing/logistics
- ✅ Worth it for professionals who benefit from hands-free information access
- ⚠️ Maybe for general consumers; technology still maturing
- ❌ Not yet if you expect full AR like sci-fi movies
Current best value: Audio smart glasses ($200-$300) or AI smart glasses with camera ($300-$400)
Do I need a smartphone to use smart glasses?
Most consumer smart glasses require a smartphone for full functionality:
- Smartphone provides processing power
- Handles internet connectivity
- Stores media and runs apps
- Configures settings
Exceptions:
- Some enterprise models have standalone LTE
- Audio glasses work independently for music playback
- Future models trend toward standalone operation
How long do smart glasses batteries last?
Typical battery life in 2025:
- Audio only: 6-12 hours
- Notifications + light use: 4-8 hours
- AR display active: 2-4 hours
- Video recording: 1-3 hours continuous
Battery life improving year over year, with all-day use expected by 2026-2027 for most use cases.
Can I get prescription lenses for smart glasses?
Yes, but with limitations:
- Many models offer prescription lens options
- Typically add $100-$300 to base price
- Available for single vision and some progressive prescriptions
- Strong prescriptions may not be compatible with all models
- Order through manufacturer or authorized optical partners
Are smart glasses safe for my eyes?
Generally yes, when used responsibly:
- Display brightness similar to phone screens
- Blue light exposure comparable to other digital devices
- No evidence of increased eye strain vs. smartphones
- Follow 20-20-20 rule: every 20 minutes, look 20 feet away for 20 seconds
Consult eye doctor if:
- You experience persistent eye strain
- You have pre-existing eye conditions
- You’re using AR displays extensively (>4 hours/day)
What about privacy concerns?
Smart glasses raise legitimate privacy concerns:
- Recording without clear indication
- Facial recognition capabilities
- Data collection by manufacturers
- Use in private spaces
Protect privacy:
- Choose models with recording indicators
- Follow local recording laws
- Respect others’ privacy in shared spaces
- Review manufacturer privacy policies
- Disable features you don’t need
Conclusion: The Smart Glasses Journey Ahead
Smart glasses have evolved from ambitious but premature experiments into practical devices serving real needs across consumer and enterprise markets. While we’re still years away from the seamless AR experiences of science fiction, today’s smart glasses offer genuine value for specific use cases—from hands-free work instructions that improve manufacturing efficiency by 30%, to audio glasses that let you enjoy music while staying aware of your surroundings.
The key to a successful smart glasses experience in 2025 is matching the right device to your actual needs. Don’t buy AR smart glasses if audio-only will serve you better. Don’t invest in enterprise models for casual consumer use. And don’t expect technology that isn’t quite ready yet.
As display technology improves, batteries last longer, AI becomes more contextual, and social acceptance grows, smart glasses will gradually transition from niche devices to mainstream computing platforms. The journey has begun, and while the destination remains years away, each generation of smart glasses brings us closer to truly seamless wearable computing.