Introduction: The Dawn of Smart Eyewear Revolution
Augmented reality (AR) and artificial intelligence (AI) smart glasses represent one of the most transformative technological innovations of the 2020s. Unlike virtual reality headsets that completely immerse users in digital worlds, AR/AI smart glasses overlay digital information onto the real world while maintaining natural vision and mobility.
The smart glasses market reached $5.2 billion in 2024 and is projected to exceed $18 billion by 2028, driven by advances in micro-display technology, AI integration, and miniaturized sensors. Whether you’re a business professional seeking hands-free productivity tools or a tech enthusiast exploring cutting-edge wearables, understanding AR/AI smart glasses is essential for navigating tomorrow’s digital landscape.
This comprehensive guide explores the technology behind smart glasses, their practical applications, leading models, and critical buying considerations. For a broader overview of all smart glasses types, see our smart glasses overview.
What Are AR/AI Smart Glasses? Understanding the Technology
Defining AR Smart Glasses: More Than Just Eyewear
AR Smart glasses are wearable computing devices built into eyeglass frames that integrate miniaturized electronics—including displays, cameras, microphones, speakers, processors, and sensors—to augment human perception and enable hands-free computing.
Three primary categories exist:
- Audio-only AR smart glasses: Deliver sound through bone conduction or open-ear speakers
- AR display glasses: Project visual information onto transparent lenses or dedicated screens
- AI-powered camera glasses: Combine cameras with AI assistants for visual recognition and recording
The most advanced models combine all three capabilities, creating multimodal computing platforms worn on your face.
How AR Smart Glasses Work: The Technical Foundation
AR smart glasses employ sophisticated optical systems to blend digital content with real-world views. The core challenge is projecting crisp images at focal distances matching human vision while keeping devices lightweight and unobtrusive.

Waveguide optics are the most prevalent AR display method. These thin glass or polymer sheets contain microscopic gratings that channel light through total internal reflection. The process involves three stages:
- In-coupling: A micro-display projects images into the waveguide edge
- Propagation: Light bounces internally through the material via engineered angles
- Out-coupling: Positioned gratings redirect light toward the eye, creating a large virtual display
Stanford researchers found that waveguide displays manipulate light waves rather than pixels, allowing intelligent software to adjust wavefront properties so virtual objects appear at realistic depths. This differs fundamentally from traditional screens that emit pixels—waveguides create interference patterns that trick your brain into perceiving depth and distance naturally.
The engineering challenge lies in maintaining image quality across the entire eyebox (the 3D region where your eye can move while still seeing the full image). Early waveguides suffered from “rainbow artifacts”—colorful distortions at image edges—but modern designs using multiple stacked waveguides for different color channels have largely solved this issue. Companies like DigiLens and WaveOptics have refined waveguide manufacturing to achieve uniformity across mass production.
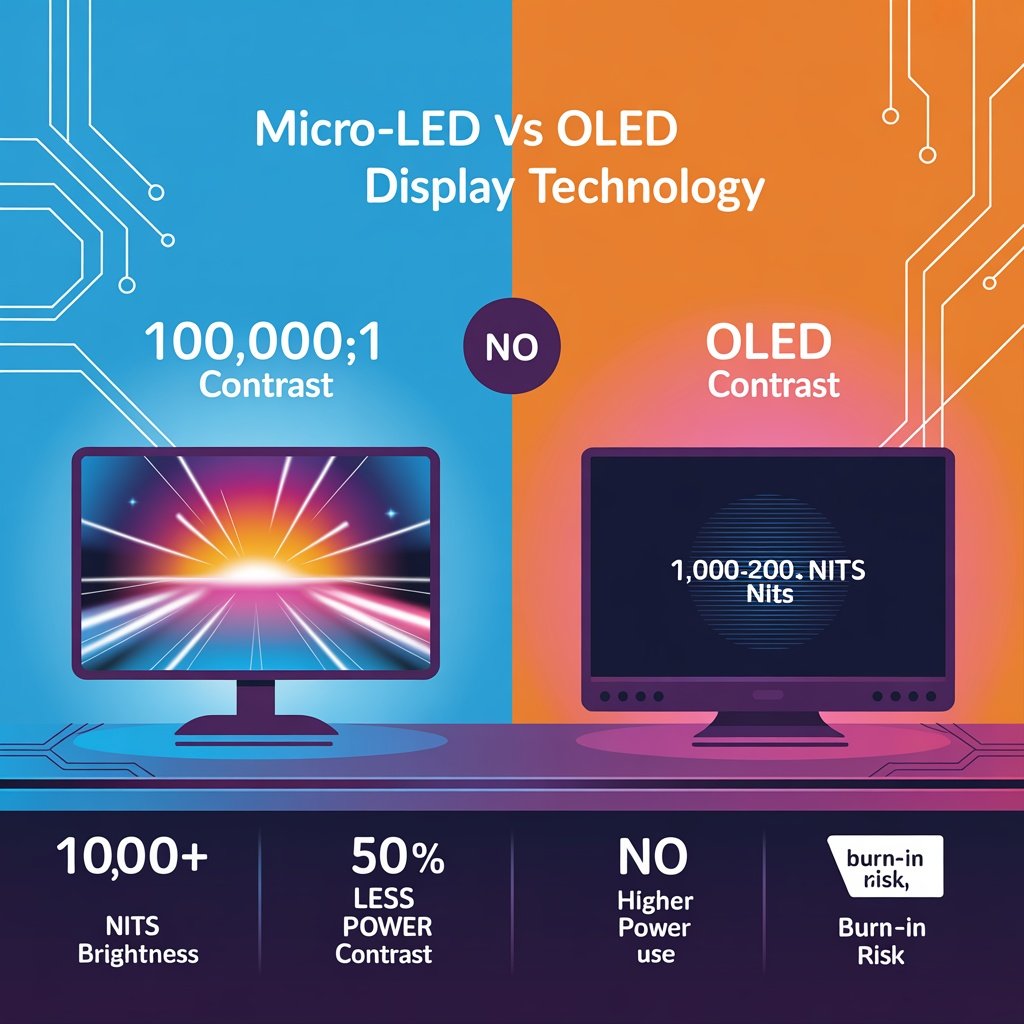
Micro-LED displays represent the next-generation light source for AR glasses. These miniature LEDs measure under 100 micrometers—smaller than a human hair—and offer superior brightness (exceeding 10,000 nits), contrast ratios above 100,000:1, faster refresh rates (over 120Hz), and 50% lower power consumption compared to OLED alternatives.
The brightness advantage proves crucial for outdoor use. Traditional smartphone screens peak at 1,000-2,000 nits, becoming difficult to read in direct sunlight. Micro-LEDs achieving 10,000+ nits ensure AR overlays remain visible even on sunny days. Additionally, micro-LEDs don’t suffer from OLED’s burn-in problem, critical for AR glasses that may display static UI elements for extended periods.
Major manufacturers including Apple, Samsung, and Sony are investing billions in micro-LED production facilities. Industry analysts predict micro-LED-based AR glasses will dominate the premium segment by 2026-2027 as manufacturing costs decrease through economies of scale.
AI Integration: From Passive Displays to Intelligent Assistants
Modern AR smart glasses increasingly incorporate AI capabilities that transform them from simple display devices into intelligent assistants. Large language models enable:
- Visual question answering: Point at objects and ask questions
- Real-time translation: See foreign text translated instantly in your field of view
- Object recognition: Identify products, landmarks, plants, or animals automatically
- Contextual assistance: Receive information based on what you’re viewing
Meta’s Ray-Ban Smart Glasses exemplify this trend, using a 12MP camera to capture what you see, sending images to Meta AI servers, and returning answers via audio. Learn more about AI smart glasses explained and how machine learning enhances visual recognition.
Sensor Arrays: Enabling Spatial Computing
Advanced AR glasses incorporate multiple sensors to understand their position and environment:
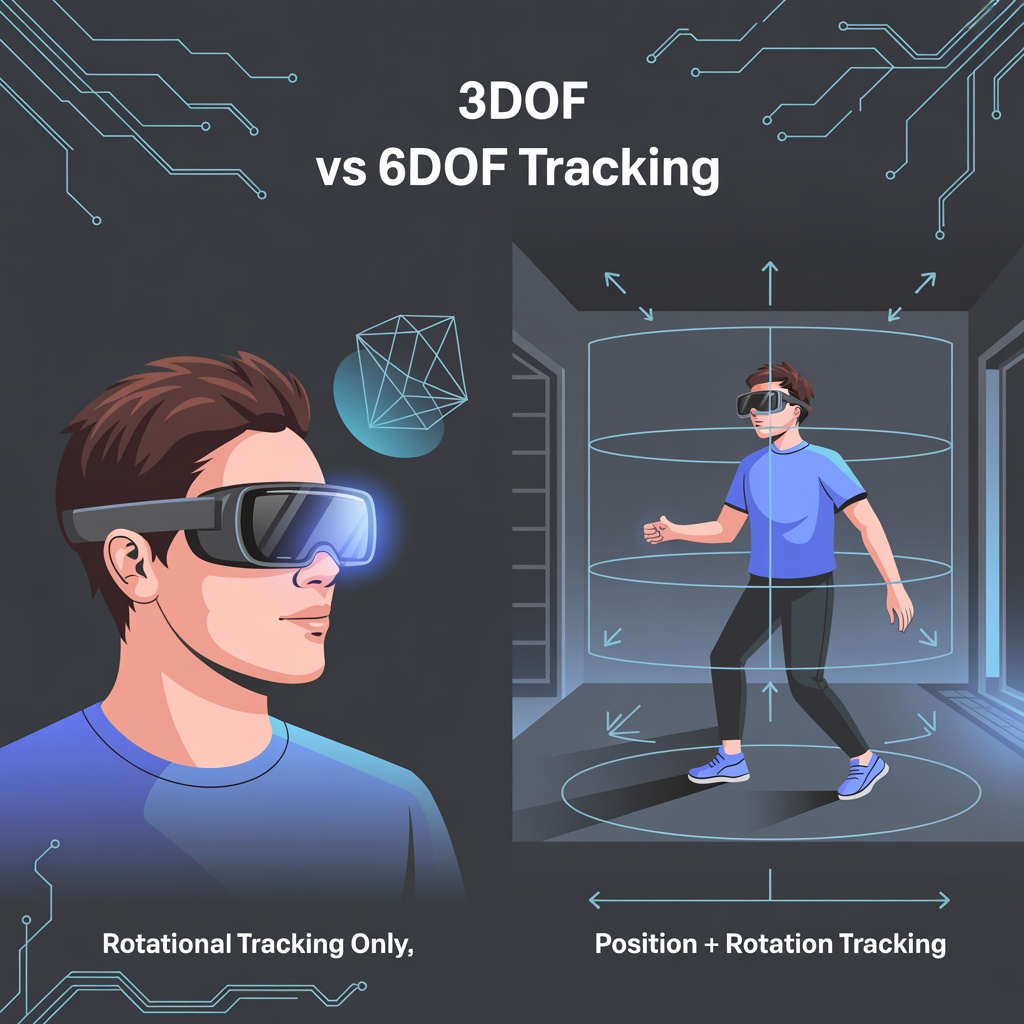
- IMU: Accelerometers and gyroscopes track head movement for 3DOF head tracking
- Cameras: Provide pass-through video, object recognition, and 6DOF positional tracking
- LiDAR: Measures distances for precise depth mapping
- Eye-tracking: Monitors gaze direction for foveated rendering and intuitive controls
The XReal One Pro demonstrates 3DOF tracking’s value: virtual displays remain anchored in space as you turn your head, mimicking the experience of watching a physical screen.
Types of AR/AI Smart Glasses: Finding Your Category
Consumer AR Display Glasses: Personal Cinema and Productivity
These glasses prioritize screen replacement, projecting large virtual displays equivalent to 100-200-inch screens viewed from several feet away.
Primary uses:
– Private movie watching on planes or at home
– Mobile productivity with virtual multi-monitor setups
– Gaming on massive personal displays
– Discrete content consumption in public spaces
Leading models:
– XReal One Pro ($599): 57-degree field of view, 1080p resolution, built-in 3DOF tracking
– Viture Luma Pro ($549): Bright 4,000-nit display, focus dials for nearsighted users
– RayNeo Air 3s Pro ($399): Budget-friendly option with vibrant colors
AI Camera AR Smart Glasses: Intelligent Life Capture
Camera-first AI smart glasses integrate AI assistants that can see what you see, answer questions, and capture first-person photos/videos.
Primary uses:
– Hands-free photography and videography
– Visual Q&A with AI assistants
– Voice-controlled assistance
– POV content creation
Leading models:
– Meta Ray-Ban Smart Glasses ($299): 12MP camera, Meta AI integration, stylish designs
– Oakley Meta Vanguard ($699): IP67 waterproof rating for extreme sports
– Solos AirGo Vision ($249): ChatGPT-4 Vision integration
Ray-Ban Meta glasses dominated 2024 sales, capturing over 60% market share by focusing on fashion and practicality rather than futuristic aesthetics.
Enterprise AR Headsets: Industrial and Professional Tools
Business-focused AR devices prioritize functionality over style, offering wider fields of view, advanced hand tracking, and rugged construction.
Primary applications:
– Manufacturing assembly with visual work instructions
– Remote expert assistance for field technicians
– Medical training and surgical planning
– Warehouse picking and logistics optimization
Leading platforms:
– Microsoft HoloLens 2 ($3,500): 52-degree FOV, hand tracking, 6DOF spatial computing
– Magic Leap 2 ($3,299): Dimming technology for bright environments
– Vuzix Z100 ($999): Lightweight enterprise option with waveguide displays
A 2024 PTC study found AR-assisted manufacturing workers completed tasks 32% faster with 90% fewer errors compared to paper instructions.
Key Features and Specifications: What to Look For
Display Technology and Field of View (FOV)
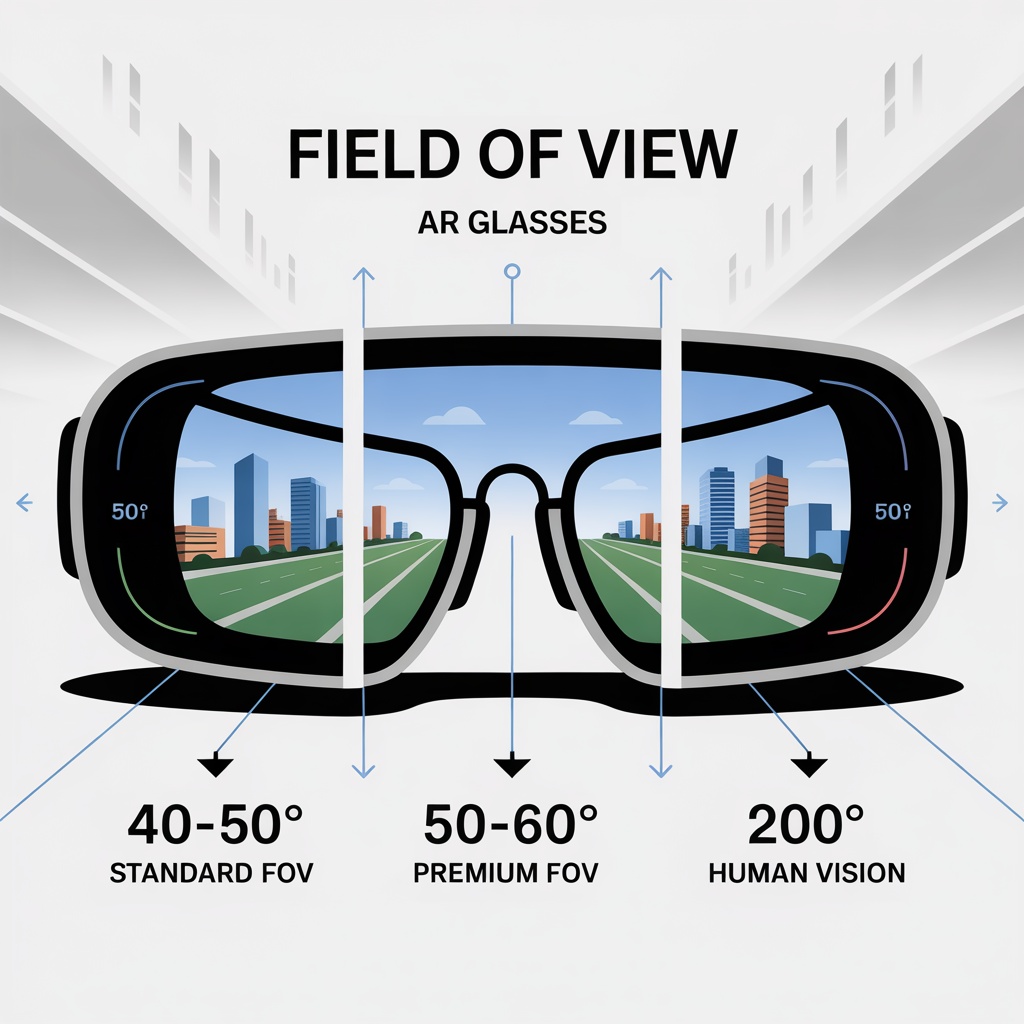
Field of view determines how much of your vision displays digital content:
- 40-50 degrees: Standard for consumer AR glasses
- 50-60 degrees: Premium range offering more immersive experiences
- 100+ degrees: Enterprise headsets and VR devices
Human binocular vision spans approximately 200 degrees horizontally, so even the widest AR glasses show content within a limited “window.”
Resolution matters equally:
– 1080p (1920×1080) per eye: Standard quality, adequate for text and video
– 1200p (1920×1200) per eye: Crisper text rendering, better for productivity
– 2K+ (2560×1440+) per eye: Premium clarity for detailed work
Pay attention to pixels per degree (PPD)—a metric measuring sharpness. Human eyes perceive around 60 PPD for 20/20 vision. Most AR glasses achieve 25-35 PPD, making small text slightly blurry.
AR Glasses Display Comparison Table:
| Model | FOV | Resolution | PPD | Brightness | Weight |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| XReal One Pro | 57° | 1920×1080 | ~34 | 1,800 nits | 85g |
| Viture Luma Pro | 52° | 1920×1200 | ~37 | 4,000 nits | 78g |
| RayNeo Air 3s Pro | 46° | 1920×1080 | ~42 | 1,600 nits | 78g |
| Microsoft HoloLens 2 | 52° | 2048×1080 | ~47 | 500 nits | 566g |
| Meta Quest 3 (VR comparison) | 110° | 2064×2208 | ~25 | ~100 nits | 515g |
Notice the trade-offs: higher FOV typically means lower PPD unless resolution increases proportionally. The RayNeo Air 3s Pro achieves the highest PPD among consumer models through its narrower FOV, making text exceptionally crisp despite the smaller viewing window. For technical details on waveguide optics and micro-LED technology, explore our display technology deep dive.
To understand the complete working principle from sensors to displays, check our guide on how AR displays work.
Audio Systems: Open-Ear vs. Bone Conduction
Open-ear directional speakers use precisely aimed micro-speakers near your ears. Advanced models employ beam-forming technology to focus sound waves toward your ear canals, creating a “personal audio bubble.”
Bone conduction transducers vibrate cheekbones to transmit sound directly through skull bones to the inner ear, leaving ear canals completely open. This technology ensures maximum environmental awareness—critical for cyclists, runners, or anyone needing to hear traffic, warnings, or conversations while listening to content.
The trade-off involves audio quality. Bone conduction typically delivers weaker bass response, less dynamic range, and slightly uncomfortable vibrations at high volumes. Testing from PCMag found Ray-Ban Meta’s open-ear speakers produced “surprisingly full audio with decent bass,” while Chamelo Music Shield’s bone conduction system sounded “tinny” but excelled at maintaining situational awareness.
Audio leakage comparison: At normal listening volumes (60-70% maximum), open-ear speakers leak faintly audible sound to people within 1-2 feet. Someone sitting directly next to you on a plane might detect you’re playing audio but won’t discern content. Bone conduction produces minimal external sound, though the vibrations themselves can feel unusual during extended wear.
Battery Life and Charging
Smart glasses battery performance varies dramatically:
Display-focused glasses typically draw power directly from connected devices via USB-C, eliminating battery concerns. Their built-in batteries serve primarily for brief untethered sessions (1-2 hours).
AI camera glasses contain integrated batteries lasting:
– 4-6 hours of mixed audio, AI queries, and occasional photos
– 2-3 hours of continuous video recording
– Up to 36 hours in standby mode with charging case
Privacy and Security Features
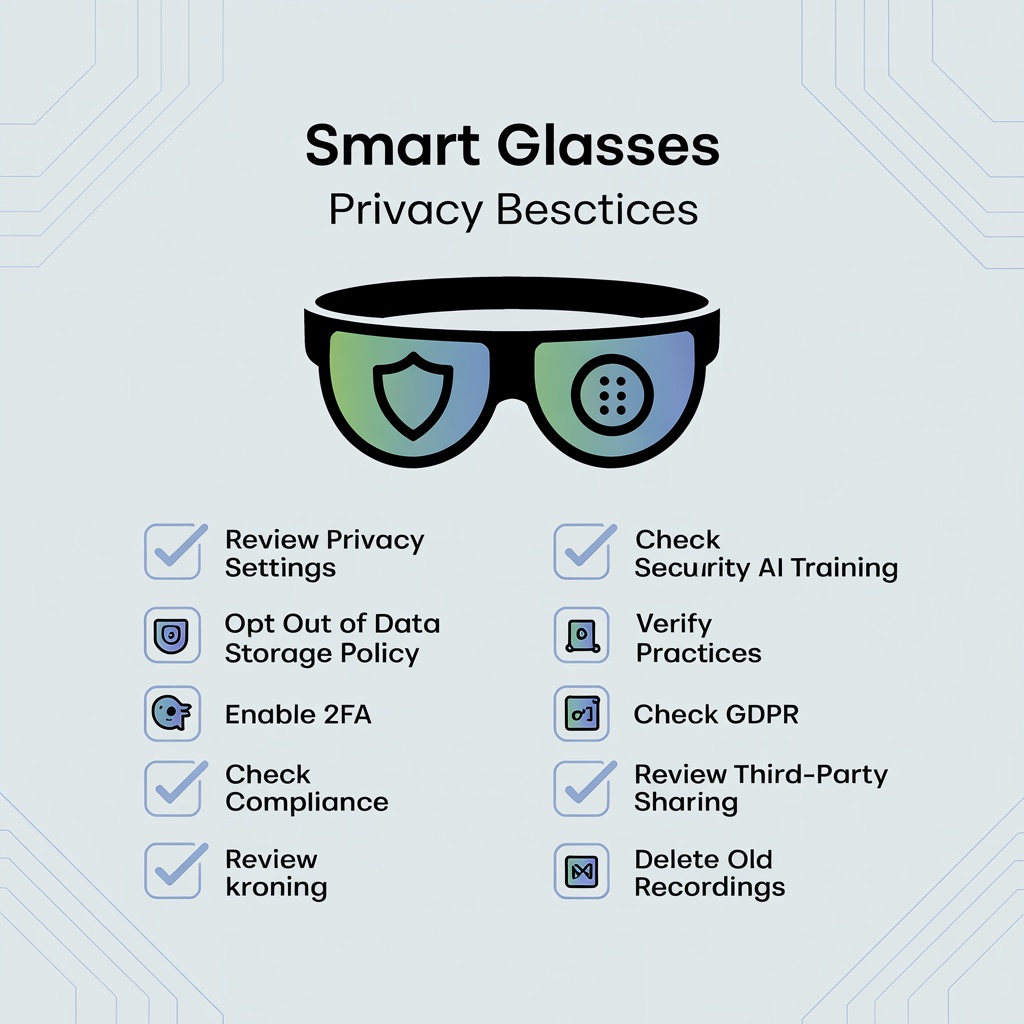
Key protective features include:
Visual recording indicators: LED lights that illuminate when cameras activate. Meta Ray-Ban glasses feature a prominent white LED that cannot be disabled, alerting others to potential recording.
Voice-only AI modes: Some glasses offer AI assistance without camera access, reducing privacy risks.
On-device processing: Premium models process some AI functions locally rather than uploading all data to cloud servers.
Data encryption and access controls: Enterprise AR glasses typically include biometric authentication, encrypted storage, and company-controlled data policies.
The Electronic Frontier Foundation warns that AI camera glasses pose significant privacy risks, enabling continuous data harvesting in public spaces. The report emphasized that recording indicators, while helpful, don’t address the fundamental issue: the normalization of constant surveillance.
Data privacy considerations checklist:
☐ Review and opt out of AI training data collection in privacy settings
☐ Understand what data the manufacturer stores and for how long
☐ Check if processing happens on-device or requires cloud uploads
☐ Verify the company’s data breach history and security practices
☐ Consider jurisdictional privacy laws (GDPR in Europe offers more protection)
☐ Read the privacy policy’s fine print about third-party data sharing
☐ Enable two-factor authentication on associated accounts
☐ Regularly review and delete stored recordings you don’t need
Most users never adjust privacy settings beyond defaults, which typically maximize data collection for manufacturers. Taking 10-15 minutes to configure privacy options significantly reduces your data exposure.
Practical Applications: How People Use AR Smart Glasses
Consumer Use Cases
Private entertainment systems: The most popular consumer application involves watching movies or shows on large virtual screens without disturbing others. Travelers particularly value this feature on long flights.
Navigation and wayfinding: AR glasses can overlay directional arrows onto real streets, eliminating constant smartphone checking while walking or driving. Google Maps AR navigation, available on select AR smart glasses, shows 3D arrows floating above streets at the exact turn points, significantly reducing navigation errors compared to traditional 2D maps.
This proves especially valuable in complex urban environments with multi-level intersections or confusing highway exits. Instead of glancing down at your phone every few seconds—a dangerous habit while walking busy streets or driving—you maintain natural forward vision while arrows guide you. Early testers report arriving at destinations faster and with significantly less stress, particularly in unfamiliar cities.
Language translation: Point glasses at foreign text and see instant translations—invaluable for travelers navigating restaurants, signs, or products. Learn about real-time translation capabilities and supported languages.
Fitness tracking: Specialized sports glasses display real-time performance metrics—pace, heart rate, power output—without requiring wrist-checking.
Social media content creation: Creators capture authentic POV footage for Instagram, TikTok, and YouTube without handheld cameras.
Business and Professional Applications

Remote expert assistance: Field technicians wearing AR glasses stream their first-person view to remote experts who can annotate the live video feed in real-time, highlighting specific components, drawing arrows, or overlaying diagrams. This “see what I see” capability proves invaluable for complex repairs or installations requiring specialized knowledge.
Boeing implemented this system for aircraft assembly, reporting 25% reduction in wiring harness installation time and virtually eliminating errors that previously required costly rework. A senior technician in Seattle can guide junior technicians in multiple facilities simultaneously, multiplying expert knowledge across the organization. Similarly, medical device companies use AR remote assistance to guide hospital technicians through equipment repairs without dispatching expensive specialists.
Hands-free documentation: Workers in manufacturing, logistics, or healthcare use voice commands to document processes or capture inspection photos without stopping work.
Training and skills transfer: New employees learn faster with AR-guided step-by-step instructions overlaid directly on physical equipment they’re working on. Instead of consulting paper manuals or computer screens positioned away from the work area, trainees see contextual instructions precisely where they need them—arrows pointing to specific bolts, warnings highlighting fragile components, or animations demonstrating proper technique.
Porsche implemented AR training for complex engine repairs, reducing the training period for new technicians from several months to just weeks while simultaneously improving quality metrics. The system tracks trainee performance, identifying skills that need additional practice and automatically adjusting instruction difficulty. Early results show technicians trained with AR maintain higher performance levels years after initial training compared to traditionally trained counterparts.
Pick-and-pack operations: Warehouse workers see digital indicators highlighting which items to select and optimal routes. DHL reported 25% productivity gains after deploying AR glasses.
Surgical assistance: Surgeons use AR headsets displaying patient vitals and medical imaging without looking away from the operating field.
Accessibility Features
AR Smart glasses offer transformative possibilities for people with disabilities:
Visual assistance: AI-powered glasses describe surroundings, read text aloud, recognize faces, and navigate obstacles for people with low vision. Discover specialized accessibility features designed for visually impaired users.
Hearing augmentation: Visual alerts for doorbells, alarms, or conversations help deaf and hard-of-hearing individuals. Some models offer live speech-to-text captioning.
Mobility support: AR navigation provides detailed obstacle warnings and optimal path planning for wheelchair users or those with limited mobility.
Top AR/AI Smart Glasses Models in 2025

Best Overall: XReal One Pro
Price: $599
Best for: Power users seeking maximum screen real estate
The XReal One Pro leads 2025 rankings with an industry-best 57-degree field of view—significantly larger than competitors’ 40-50-degree offerings.
Key features:
– 57-degree FOV with 1920×1080 resolution per eye
– Built-in 3DOF head tracking (anchors display in virtual space)
– Dimmable electrochromic lenses
– Comfortable 85-gram weight
Limitations: No diopter adjustment, premium pricing, USB-C connection only
PCMag awarded it an Editors’ Choice, calling it “the most advanced video-focused AR glasses available in 2025.” Tom’s Guide concurred, noting the 3DOF tracking “fundamentally changes the AR glasses experience” by eliminating the motion sickness some users experience with head-locked displays.
Real-world performance: In extensive testing, the XReal One Pro excels for both productivity and entertainment. The ultrawide desktop mode genuinely replicates a dual-monitor setup, making it viable for coding, spreadsheet work, or creative applications. Movie watching feels remarkably immersive—the anchored display mimics sitting in a theater, and the electrochromic dimming blocks out ambient light effectively on planes or in bright rooms.
Who should buy: Power users who want maximum screen space for mobile work, frequent travelers seeking the best entertainment experience, or gaming enthusiasts wanting an immersive personal display. The premium price is justified if these use cases match your needs.
Best Value: RayNeo Air 3s Pro
Price: $399
Best for: Cost-conscious users wanting quality AR displays
The RayNeo Air 3s Pro delivers 90% of premium performance at 65% of the cost. Its 46-degree FOV and vibrant 1080p display satisfy most users for entertainment and basic productivity.
Key features:
– 46-degree FOV with exceptionally vibrant colors
– Multiple picture modes for different content
– Clear, full audio from integrated speakers
– Compact 78-gram weight
Trade-offs: No head tracking, no dimmable lenses
Best AI Camera Glasses: Meta Ray-Ban Smart Glasses
Price: $299-$379
Best for: Social media creators and AI assistant enthusiasts
Meta’s collaboration with Ray-Ban produced the first truly mainstream AR smart glasses, looking like normal Wayfarer sunglasses while packing impressive technology.
Key features:
– 12MP camera capturing 3K video
– Meta AI with visual question answering
– Open-ear directional speakers
– 4-6 hour battery life
Notable absence: No display (audio and camera only)
Meta sold over 700,000 units in 2024, capturing 60% market share. Their success stems from solving the fundamental challenge that doomed Google Glass: making AR smart glasses that people actually want to wear in public.
Real-world performance: The Meta AI integration impresses with its practical utility. Point at a restaurant and ask “What’s this place rated?” or look at a plant and query “What kind is this?” The system responds within 2-3 seconds with surprisingly accurate answers. The 12MP camera captures social-media-ready content without the awkwardness of holding up a phone—particularly valuable for action sports or hands-busy activities like cooking.
Privacy considerations: The prominent LED recording indicator helps address privacy concerns, though some establishments still prohibit them. Be prepared for occasional questions or requests to remove them in sensitive environments. For comprehensive guidance on recording laws and ethical use, consult our camera specifications guide and camera privacy concerns resource.
Who should buy: Social media creators wanting authentic POV content, tech enthusiasts excited about AI assistants, or anyone seeking stylish sunglasses with bonus smart features. The lack of a display may disappoint those expecting visual AR overlays.
Best for Sports: Oakley Meta Vanguard
Price: $699
Best for: Athletes and outdoor enthusiasts
Oakley applied its sports optics expertise to Meta’s platform, creating the most durable option available with IP67 waterproof rating.
Key features:
– Full IP67 dust and water resistance
– Same Meta AI and camera features as Ray-Ban version
– Customizable action button
– Interchangeable Prizm sport lenses
Downsides: Premium price, shorter battery life (3-4 hours)
Best for Business: Vuzix Z100
Price: $999
Best for: Enterprise users requiring lightweight AR displays
The Vuzix Z100 targets businesses with professional aesthetics, comfortable all-day wear, and enterprise-grade software compatibility.
Key features:
– Waveguide display for AR overlays
– 40-degree FOV optimized for text and data
– 6DOF tracking with built-in cameras
– Hot-swappable battery modules
Vuzix has supplied over 50,000 units to Fortune 500 companies.
Buying Guide: Choosing the Right AR Smart Glasses
Determining Your Primary Use Case
Choose display-focused AR glasses if you want:
– A personal cinema for travel or home entertainment
– Expanded screen real estate for mobile productivity
– Gaming on large virtual displays
Choose AI camera glasses if you want:
– Hands-free photography and videography
– An AI assistant that sees what you see
– Social media content creation
Choose enterprise AR headsets if you need:
– Industrial applications with work instructions
– Remote expert collaboration
– Professional reliability and support
Understanding Optical Considerations
For nearsighted users (myopia):
– Look for models with adjustable focus dials (e.g., Viture Luma Pro adjusts to -4.0 diopters)
– Budget extra for prescription lens inserts (typically $79-$149)
For farsighted users (hyperopia):
– Most AR glasses focus virtual displays at 2-4 meters
– Fewer accommodation options exist
For astigmatism:
– Prescription lens inserts are essential
– Confirm your prescription is within manufacturer’s supported range
Try before buying if possible. Best Buy and some Ray-Ban stores offer in-person demos of select models. This hands-on experience proves invaluable—AR smart glasses comfort and visual quality vary significantly between individuals based on facial structure, interpupillary distance (IPD), and vision characteristics. What works perfectly for one person may feel uncomfortable or look blurry to another.
Key fitting considerations:
– Nose bridge fit: Too tight causes discomfort after 30-60 minutes; too loose causes slipping
– Temple pressure: Should feel secure without creating pressure points
– Weight distribution: Well-designed glasses distribute weight across ears and nose evenly
– IPD compatibility: Your interpupillary distance should match the glasses’ fixed lens spacing for optimal image clarity
Privacy and Social Considerations

AR Smart glasses’ social acceptance varies by context and design. Meta’s Ray-Ban Wayfarers blend into everyday fashion, while bulkier AR headsets draw attention.
Questions to consider:
– How would you feel about others recording you without explicit consent?
– Will you wear AR smart glasses in sensitive environments?
– Do your friends/family express discomfort with camera glasses?
Privacy concerns remain widespread about people wearing camera glasses in public spaces, with many feeling uncomfortable even with recording indicators present. This sentiment creates real social friction for early adopters.
Practical social navigation tips:
– Inform friends/family before wearing camera glasses around them
– Remove them in clearly sensitive environments (locker rooms, medical offices, schools)
– Be prepared to explain the technology to curious or concerned individuals
– Consider display-only AR glasses if camera features aren’t essential
– Respect establishment policies prohibiting recording devices
Some early adopters report the social acceptance varies significantly by context—wearing Meta Ray-Ban glasses at a beach or outdoor concert draws little attention, while the same glasses in a gym or coffee shop sometimes prompt questions or discomfort.
Ecosystem and Compatibility
For Apple users:
– XReal and Viture offer robust iOS compatibility
– Meta Ray-Ban glasses integrate with Instagram/WhatsApp
For Android users:
– Most AR display glasses work seamlessly via USB-C
– Meta Ray-Ban glasses offer fuller feature sets on Android
– Explore our Bluetooth connectivity guide for pairing instructions and wireless features
For PC users:
– AR display glasses excel as external monitors
– Enterprise headsets integrate with business software
Budget and Total Cost of Ownership
Hidden costs include:
– Prescription lens inserts: $79-$149
– Premium carrying cases: $29-$79
– Replacement accessories: $15-$40
– Wireless adapters: $49-$99
– Extended warranties: $79-$149
A $399 AR display purchase can easily become $550-$600 with necessary accessories. Budget accordingly when comparing models—sometimes a more expensive model with included accessories offers better total value than cheaper options requiring extensive add-ons.
Recurring costs to consider:
– Battery replacement: Non-replaceable batteries degrade after 2-3 years, requiring manufacturer service ($79-$129)
– Lens replacement: Scratched external lenses need replacement every 1-2 years with active use ($49-$99)
– Software subscriptions: Some enterprise models charge monthly fees for cloud services ($10-$50/month)
– Accessory updates: New carrying cases, cables, or adapters as technology evolves
Resale value reality: AR smart glasses depreciate faster than smartphones due to rapid technological advancement. Expect 40-60% value loss within 12 months. The limited secondary market means you’ll likely need to use platforms like eBay or specialty tech resale sites rather than convenient trade-in programs.
Limitations and Challenges
Technical Limitations
Battery life remains inadequate for all-day use. Most AR display glasses achieve 2-3 hours of continuous operation, while camera glasses last 4-6 hours.
Processing power pales compared to smartphones, meaning most AI features require cloud connectivity, introducing latency and privacy concerns.
Display brightness struggles in direct sunlight. Even the brightest AR glasses become difficult to see outdoors on sunny days.
Field of view remains narrow compared to human vision. The best consumer AR glasses show content across 57 degrees—less than one-third of natural binocular vision (~200 degrees).
Social and Cultural Barriers
The “Glasshole” effect persists from Google Glass’s 2013 failure. Early adopters faced social backlash for wearing camera-equipped eyewear in public.
Privacy concerns undermine trust. Even when not recording, camera glasses make others uncomfortable.
Fashion barriers limit appeal. Many people view eyewear as personal expression. Current AR smart glasses offer limited aesthetic variety compared to traditional eyewear.
Privacy and Security Concerns
Always-on cameras enable covert recording that erodes public privacy. While recording indicators help, they’re insufficient.
Data collection practices remain opaque. Meta’s privacy policy allows using Ray-Ban glasses data to train AI models unless users explicitly opt out.
Security vulnerabilities could transform glasses into spying tools. Researchers have demonstrated hacking various models to remotely activate cameras.
Regulatory gaps mean few legal protections exist. No comprehensive U.S. federal laws specifically address smart AR glasses privacy concerns.
The Future of AR/AI Smart Glasses

Near-Term Developments (2025-2027)
Integrated displays in lightweight frames: Meta previewed prototype Ray-Ban glasses with built-in micro-LED displays, promising commercial release in 2025-2026.
Enhanced AI capabilities: GPT-5 and Gemini 2.0 integration will enable more sophisticated visual understanding and real-time translation.
Expanded field of view: Next-generation waveguide technology targets 80-100-degree FOV while maintaining lightweight form factors.
Prescription integration: Manufacturers will offer seamless prescription lens integration at purchase time.
Medium-Term Vision (2027-2030)
All-day battery life: Solid-state battery technology could extend operation to 12-16 hours—matching smartphone standards.
True hand gesture control: Advanced computer vision will enable precise hand tracking for manipulating holographic interfaces.
5G and edge computing integration: Ultra-low-latency networks will enable real-time AI processing without cloud round-trips.
Long-Term Possibilities (2030+)
Contact lens displays: Companies like Mojo Vision are developing AR contact lenses with integrated micro-displays.
Holographic projection: Future AR smart glasses might project holographic images visible to multiple people simultaneously.
Sensory augmentation beyond vision: AR smart glasses could evolve into comprehensive sensory enhancement platforms.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: Can I use AR smart glasses if I wear prescription glasses?
A: Yes, through several options: prescription lens inserts ($79-$149), adjustable focus dials (like Viture Luma Pro for up to -4.0 diopters), or wearing contact lenses underneath.
Q: Do AR smart glasses work with iPhones and Android equally well?
A: AR display glasses generally work identically across iOS and Android. AI camera glasses like Meta Ray-Ban offer fuller feature sets on Android.
Q: How do people know if I’m recording?
A: Responsible manufacturers include visible recording indicators—Meta Ray-Ban glasses feature a prominent white LED during capture. However, no foolproof solution exists.
Q: What’s the difference between AR glasses and VR headsets?
A: AR glasses overlay digital information onto real-world views, maintaining awareness of surroundings. VR headsets completely block out reality, immersing you in fully digital environments.
Q: How long do batteries last?
A: AR display glasses often draw power from connected devices (unlimited runtime), AI camera glasses last 4-6 hours of mixed use, and enterprise headsets achieve 2-4 hours of active operation.
Q: Are AR smart glasses safe for my eyes?
A: Current smart glasses pose minimal direct health risks when used appropriately. However, prolonged use may cause digital eye strain. Follow the 20-20-20 rule: every 20 minutes, look at something 20 feet away for 20 seconds.
Q: Can AR smart glasses replace my smartphone?
A: Not yet. Current smart glasses function as smartphone accessories rather than replacements, requiring paired phones for cellular connectivity and most functionality.
Q: What happens to my data when using AI features?
A: Most AI-powered AR smart glasses send visual and audio data to cloud servers for processing. Companies may retain this data to improve AI models unless you opt out in privacy settings.
Conclusion: Are AR/AI Smart Glasses Right for You?
AR smart glasses have evolved from awkward early prototypes into genuinely useful computing platforms. While not yet ready to replace smartphones, they excel at specific use cases.
You should consider your AR smart glasses if:
– You frequently consume media during travel
– You create first-person content for social media
– Your work involves hands-free documentation or remote assistance
– You’re excited about early adoption of transformative technology
AR Smart glasses probably aren’t for you if:
– You expect a smartphone replacement
– Privacy concerns about camera-equipped wearables trouble you
– You’re sensitive to social stigma around wearing conspicuous technology
– You prefer mature, refined technology
The AR smart glasses market will continue rapid evolution. By 2027-2028, we’ll likely see all-day battery life, wider fields of view, and more powerful AI assistance—features that could drive mainstream adoption. But today’s models remain niche products for enthusiasts and specific professional applications.
About the Author:
Nelson is a technology analyst at Banna-Tech specializing in emerging wearable technologies and augmented reality systems. With over eight years of experience testing consumer electronics, Marcus provides evidence-based guidance to help readers make informed technology decisions.
References:
- Stanford News. “Augmented reality comes to regular glasses.” May 2024.
- PCMag. “The Best Smart Glasses We’ve Tested for 2025.” 2025.
- Tom’s Guide. “Best smart glasses — top AR and AI glasses to buy right now.” October 2025.
- Electronic Frontier Foundation. “Augmented Reality Must Have Augmented Privacy.” October 2020.
- PTC. “Vuforia Leads PAC’s 2024 AR Platforms for Connected Workers.” August 2024.
- The Washington Post. “Gen Z is pushing back on smart glasses recording strangers in public.” August 2025.
- SpringerOpen eLight. “Waveguide-based augmented reality displays: perspectives and challenges.” December 2023.
- MiniMicroLED. “Micro LED For Waveguides: Full-Color AR Nears Production.” August 2025.