By David Chen, AR Technology Specialist | Updated: November 18, 2025 | 9 min read
Introduction
Smart glasses technology represents one of the most sophisticated convergences of miniaturized hardware and intelligent software in modern wearable computing. Unlike their failed predecessor Google Glass (2013), today’s smart glasses integrate advanced display systems, powerful processors, AI-driven interfaces, and seamless connectivity into eyewear weighing less than 90 grams [1]. Understanding how smart glasses technology works reveals a complex ecosystem where micro-OLED displays, waveguide optics, System-on-Chip processors, and multimodal sensors collaborate to overlay digital information onto the physical world.
This comprehensive guide dissects the complete technology stack powering smart glasses in 2025—from the silicon carbide waveguides in Meta’s Orion to the generative AI models running on Qualcomm’s Snapdragon AR chips. Whether you’re evaluating smart glasses for enterprise deployment, developing AR applications, or simply curious about the engineering behind Ray-Ban Meta’s 12MP camera system, this technical deep-dive provides the architectural blueprint you need.
Part 1: Hardware Architecture – The Physical Foundation
1.1 Display Technology: The Visual Engine
Modern smart glasses employ three primary display architectures, each with distinct optical pathways and use cases.
MicroLED + Waveguide Optics
MicroLED technology has emerged as the premium display solution for AR smart glasses, offering superior brightness (up to 5,000 nits), contrast ratios exceeding 100,000:1, and power efficiency 2-3x better than micro-OLED [2]. Companies like JBD (Jade Bird Display) lead microLED microdisplay production, with their 0.13-inch displays achieving pixel densities of 5,000+ PPI (pixels per inch).
Waveguide Integration:
Waveguides act as transparent optical channels etched with nanoscale diffraction gratings. When microLED light enters the waveguide at precise angles (typically 45-60°), total internal reflection propagates the image across the lens surface before redirecting it toward the user’s eye. Meta’s Orion glasses utilize silicon carbide waveguides with a refractive index above 2.6, enabling field-of-view (FOV) expansion beyond 70°—compared to 40-50° in conventional glass waveguides [3].
Key Specifications (2025 Standards):
- Resolution: 1920×1080 per eye (1080p minimum)
- Brightness: 2,000-5,000 nits (outdoor visibility threshold: 1,500 nits)
- FOV: 40-70° diagonal (Orion: 70°, XREAL One Pro: 57°)
- Refresh Rate: 90-120Hz (motion sickness prevention)
Micro-OLED Displays
Micro-OLED displays dominate the mid-tier market due to manufacturing maturity and lower cost. Sony’s ECX339A microdisplay (0.5-inch, 1920×1080) powers devices like XREAL Air 2 Pro, delivering 1,800 nits brightness through pixel-level light emission control [4]. Unlike LCDs requiring backlights, OLED’s self-emissive pixels enable true black levels and instant response times (<0.01ms).
Optical Coupling Methods:
- Birdbath optics (curved mirror reflectors)
- Pancake lenses (polarized folded optics, 40% thinner)
- Freeform prisms (custom-molded optical surfaces)
Retinal Projection (Emerging)
Laser beam scanning (LBS) projects RGB laser light directly onto the retina, eliminating the need for screens. Vuzix Shield employs waveguide-coupled LBS, achieving infinite depth of focus—your eye’s natural accommodation handles focus automatically. However, laser safety regulations limit brightness to 400-600 nits, restricting outdoor usability.
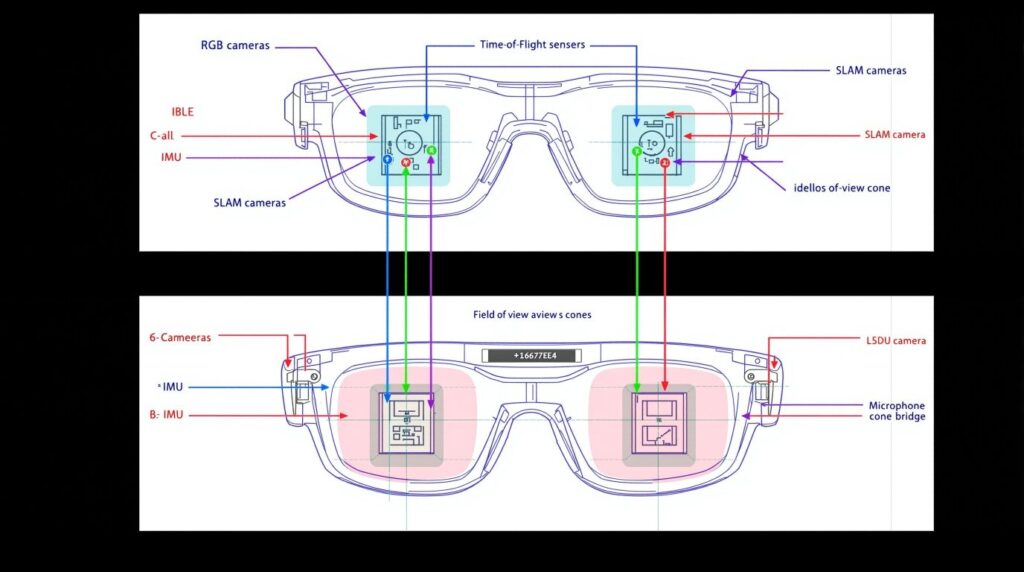
1.2 Sensor Array: Environmental Perception
Smart glasses deploy multi-sensor fusion to build real-time spatial awareness, rivaling automotive ADAS (Advanced Driver Assistance Systems) in complexity.
Inertial Measurement Unit (IMU)
9-axis IMUs combine:
- 3-axis accelerometer: Detects linear acceleration (gravity, movement)
- 3-axis gyroscope: Measures angular velocity (rotation, tilt)
- 3-axis magnetometer: Provides compass heading (magnetic north reference)
Sample Rate Performance:
Modern AR glasses use 1000Hz IMU sampling (vs. 100Hz in smartphones) to achieve sub-20ms motion-to-photon latency—the critical threshold for preventing VR sickness. Meta Quest Pro’s IMU achieves 9ms latency through predictive tracking algorithms [5].
Cameras: Visual SLAM and Scene Understanding
Stereo RGB Cameras (Ray-Ban Meta):
- Resolution: 12MP ultrawide (equivalent to 100° horizontal FOV)
- Frame Rate: 1080p@30fps video, 4K photo capture
- Use Cases: Content creation, visual search (Circle to Search), object recognition
Depth Cameras (Time-of-Flight):
ToF sensors emit infrared pulses and measure reflection time, generating depth maps at 60fps. RealWear Navigator 520’s ToF camera enables precise hand tracking within 0.2-2.0 meters, with ±1cm depth accuracy [6].
SLAM Cameras (Simultaneous Localization and Mapping):
Monochrome global shutter cameras (typically 640×480@60fps) track environmental features for inside-out positional tracking. Microsoft HoloLens 2 employs four SLAM cameras for 6DoF (six degrees of freedom) tracking with 1mm precision.
Microphone Array: Spatial Audio Processing
Beamforming microphone arrays (2-4 mics) isolate voice commands from ambient noise using:
- Acoustic echo cancellation (AEC): Removes speaker output from mic input
- Noise suppression: Attenuates steady-state noise (fan hum, traffic)
- Directional gain: Amplifies sound from 60° frontal cone by 10-15dB
Ray-Ban Meta’s 5-mic array achieves 95%+ wake word detection accuracy in 70dB environments (busy café noise level) [7].
1.3 Processing Power: The Silicon Brain
System-on-Chip (SoC) Architecture
Qualcomm Snapdragon XR2 Gen 2 (2024-2025 flagship):
- CPU: Kryo 8-core (1x 3.36GHz + 4x 2.8GHz + 3x 2.0GHz)
- GPU: Adreno 740, 2.5 TFLOPS (1440p@90fps sustained)
- AI Engine: Hexagon NPU, 12 TOPS (trillions of operations per second)
- Process Node: 4nm TSMC (40% power reduction vs. XR2 Gen 1)
AI Acceleration:
Dedicated NPU blocks handle:
- Pose estimation (skeletal tracking, 30fps)
- Semantic segmentation (real-time scene labeling)
- Object detection (YOLO models, 60fps)
- Eye tracking (120Hz gaze prediction)
Power Envelope Management:
Smart glasses target 3-8W total system power, requiring aggressive thermal design. Qualcomm’s “Smart Thermal Control” throttles CPU/GPU during sustained loads, prioritizing display refresh and sensor processing. Meta Orion employs vapor chamber cooling (0.3mm thin) to dissipate 6W while maintaining <40°C temple temperatures [8].
Memory and Storage
Typical Configuration (2025):
- RAM: 8-12GB LPDDR5 (6400 MT/s bandwidth)
- Storage: 128-256GB UFS 3.1 (2,100 MB/s sequential read)
- Display Buffer: Dedicated 2GB framebuffer for low-latency rendering
Data Throughput Example:
At 1440p@120fps with 8-bit RGB color:
- Pixel count: 2560 × 1440 × 120fps × 3 bytes = 1.3 GB/s
- With compression (DSC): ~400 MB/s sustained
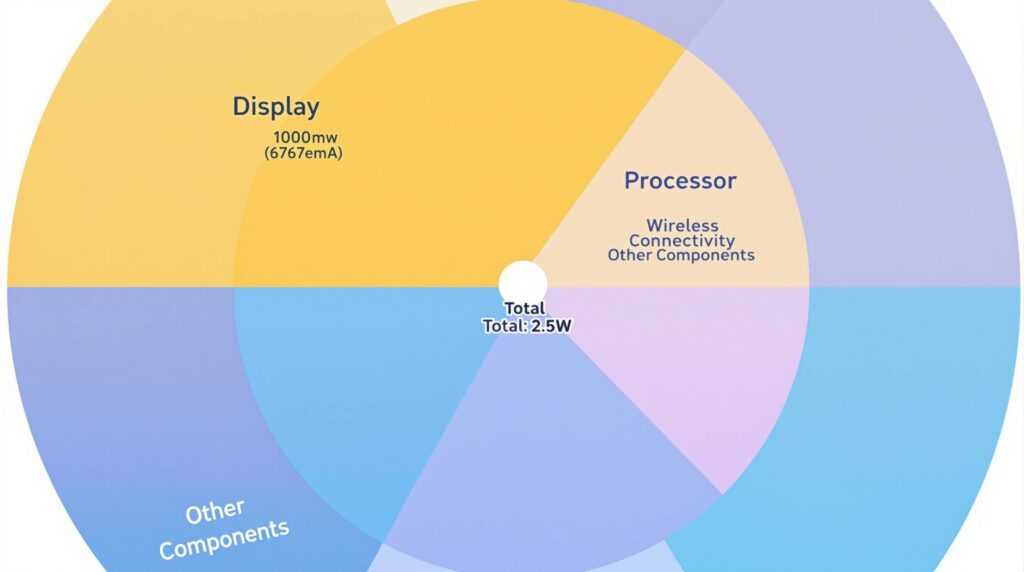
1.4 Battery and Power Systems
Battery Technology
Lithium Polymer (LiPo) Cells:
- Capacity: 500-800mAh (temple-mounted, 1.85Wh typical)
- Chemistry: Cobalt-based (higher energy density) vs. LFP (safer, lower density)
- Form Factor: Prismatic (flat rectangular) or cylindrical (temple arms)
Battery Life Calculations:
Runtime = (Battery Capacity × Voltage) / Average Power Consumption Example (Ray-Ban Meta): Runtime = (800mAh × 3.7V) / 2.5W ≈ 4.5 hours (mixed use)
Charging Solutions:
- Pogo Pin Contacts: 5V/1A (5W) charging in protective case
- Wireless Qi Charging: 5-10W (10-15% efficiency loss)
- Fast Charging: USB-C PD 3.0, 0-80% in 45 minutes
Power Optimization Strategies:
- Display dimming (auto-brightness: 30% power reduction)
- Sensor gating (IMU sleep mode when stationary)
- CPU throttling (reduce clock speed during idle)
- Wi-Fi power save mode (beacon interval optimization)
Part 2: Software Architecture – The Intelligence Layer
2.1 Operating Systems: Platform Foundations
Android XR (Google, 2024-2025)
Google’s Android XR represents the first purpose-built OS for extended reality devices, diverging from smartphone Android’s touch-centric paradigm [9].
Core Architecture:
- Kernel: Linux 6.1 with real-time scheduling patches
- Runtime: ART (Android Runtime) with JIT/AOT compilation
- XR Services: OpenXR 1.1 API layer (cross-platform VR/AR standard)
- AI Framework: TensorFlow Lite, MediaPipe (on-device inference)
Key Differentiators:
- Spatial UI Framework: 3D window manager with depth sorting
- Gemini Integration: Multimodal AI assistant (voice, vision, context)
- Privacy Controls: Camera/mic indicators, per-app permissions
- Ecosystem: Google Play XR (dedicated app store)
Partner Devices:
Samsung’s Project Moohan headset (Q4 2025) and Google’s in-house smart glasses (2026) will launch with Android XR, targeting 50+ third-party devices by 2027 [10].
visionOS Variant (Apple, Speculated 2027)
Apple’s smart glasses strategy focuses on lightweight “Apple Glass” launching 2027-2028, likely running a visionOS derivative optimized for all-day wearability. Expected features include:
- EyeSight-Lite: Simplified outward display (showing eyes, not full face render)
- Siri Proactive: Predictive AI using on-device LLM (large language model)
- HealthKit Integration: Heart rate, SpO2, temperature monitoring
- Seamless Handoff: AirPlay-style content transfer between devices
Proprietary OS (Meta, Snap)
Meta’s custom RTOS (Real-Time Operating System) for Ray-Ban Meta prioritizes:
- Boot Time: <3 seconds from cold start
- Power Efficiency: 50% lower overhead vs. Android
- AI Pipeline: Direct NPU access for Meta AI queries
2.2 AI and Machine Learning: The Cognitive Engine
On-Device AI Processing
Qualcomm’s Hexagon NPU Capabilities:
- Model Size: Run 1-7B parameter LLMs (e.g., Llama 2 7B quantized to 4-bit)
- Inference Speed: 20 tokens/second for text generation
- Vision Models: YOLOv8 object detection @ 60fps, MobileNet image classification @ 120fps
Use Cases:
- Visual Search: Point glasses at object → on-device model classifies → cloud retrieves details
- Real-Time Translation: Speech → on-device ASR (automatic speech recognition) → cloud NMT (neural machine translation) → TTS (text-to-speech)
- Contextual Reminders: “Where did I put my keys?” → on-device visual memory search
Cloud AI Integration
Hybrid Architecture:
- Edge Processing: Lightweight tasks (<100ms latency requirement)
- Cloud Offload: Complex reasoning, real-time data (weather, news)
Example Pipeline (Meta AI Query):
User: "Summarize this email" 1. Glasses capture voice (local) 2. ASR converts to text (local, 50ms) 3. Text + context sent to Meta's servers (100ms) 4. Llama 3 70B generates summary (500ms) 5. Response streamed back (100ms) Total latency: ~750ms
Privacy Considerations:
- Opt-In Cloud Processing: Users can disable cloud AI (local-only mode)
- Differential Privacy: Aggregate data anonymization (ε-differential privacy)
- Encrypted Transport: TLS 1.3 with certificate pinning
2.3 Connectivity: The Digital Lifeline
Wireless Protocols
Bluetooth 5.3 (Primary Link):
- Classic BR/EDR: Audio streaming (SBC, AAC codecs), 2Mbps
- BLE (Low Energy): Sensor data, notifications, <10mW power
- LE Audio: LC3 codec (2x efficiency vs. SBC), broadcast audio
Wi-Fi 6E (802.11ax):
- Frequency: 2.4GHz, 5GHz, 6GHz bands
- Throughput: Up to 1.2Gbps (6GHz channel)
- Latency: <10ms (Target Wake Time feature)
- Use Cases: Firmware updates, high-res video streaming, cloud AI
5G (Enterprise Models Only):
RealWear Navigator 520 integrates 5G Sub-6 modem (no mmWave due to power constraints), enabling:
- Telemedicine: 4K video consultation (15Mbps uplink)
- Remote Assistance: Real-time expert overlay (200ms glass-to-glass latency)
- Edge Computing: MEC (Multi-access Edge Computing) offload for AR rendering
Positioning and Localization
GPS/GNSS (Outdoor):
- Constellations: GPS (US), GLONASS (Russia), Galileo (EU), BeiDou (China)
- Accuracy: 3-5m (standard), <1m (RTK correction)
Indoor Positioning:
- Wi-Fi Fingerprinting: RSSI (signal strength) mapping, 2-5m accuracy
- UWB (Ultra-Wideband): Precise ranging, 10-30cm accuracy (Apple U1 chip)
- Visual SLAM: Camera-based localization, <1cm accuracy
Part 3: Integration and Use Cases
3.1 AR Rendering Pipeline
Frame Rendering Workflow (60fps = 16.67ms budget):
- Sensor Fusion (2ms): IMU + camera data → pose estimation
- Scene Understanding (5ms): Depth map generation, plane detection
- Application Logic (3ms): Game engine update, UI interaction
- Rendering (5ms): GPU draw calls, shader execution
- Distortion Correction (1ms): Lens distortion compensation
- Display Output (0.67ms): Frame buffer → display controller
Asynchronous Timewarp (ATW):
If frame misses 16.67ms deadline, ATW re-projects last frame using latest IMU data, maintaining 60fps while reducing judder. Oculus pioneered ATW; now standard in all XR platforms.
3.2 Real-World Applications
Enterprise Use Cases
Manufacturing (Boeing, Airbus):
- Task: Aircraft wiring inspection
- Technology: Vuzix M400 with 8MP camera + depth sensor
- ROI: 25% faster inspections, 40% fewer errors [11]
Healthcare (Mayo Clinic):
- Task: Surgical guidance overlay
- Technology: Microsoft HoloLens 2 with CT scan integration
- Outcome: 15% reduction in surgery time for complex procedures
Logistics (DHL):
- Task: Warehouse picking optimization
- Technology: Smart glasses with pick-by-vision
- Impact: 15% productivity increase, 50% faster training [12]
Consumer Applications
Navigation (Google Maps AR):
- Implementation: Live View feature uses VPS (Visual Positioning System)
- Accuracy: Combines GPS (5m) + computer vision (1m) + Street View database
- User Experience: Blue arrows overlaid on live camera feed
Translation (Even Realities G1):
- Languages: 40+ supported via Google Translate API
- Latency: 2-3 seconds for speech → translation → display
- Display: Scrolling text (120 characters visible)
Fitness Tracking (Upcoming Meta Orion):
- Sensors: IMU tracks head motion, PPG sensor (photoplethysmography) measures heart rate
- Calories: Proprietary algorithm correlates movement intensity → energy expenditure
- Integration: Syncs with Meta Quest Move app

Part 4: Technical Challenges and Future Directions
4.1 Current Limitations
Thermal Management:
Sustained AR rendering generates 5-8W heat in <50g devices. Solutions:
- Graphene heat spreaders (planar thermal conductivity: 5,000 W/m·K)
- Phase-change materials (PCM) absorb heat during peaks
- Dynamic thermal throttling (reduce brightness/fps when overheating)
Optical Artifacts:
- Rainbow effect: Waveguide diffractive grating dispersion
- Image uniformity: Brightness variation across FOV (±15% typical)
- Eye box: Limited viewing area (8-12mm diameter, requires precise alignment)
Privacy and Social Acceptance:
Ray-Ban Meta’s camera LED indicator addresses recording concerns, but 40% of surveyed users report discomfort being around smart glasses wearers [13]. Industry efforts include:
- Audio cues: Beep when recording starts
- Privacy modes: Disable camera in sensitive locations (gyms, bathrooms)
- Transparent policies: Clear data retention and sharing rules
4.2 Emerging Technologies (2025-2028)
MicroLED Direct Emission (No Waveguide):
JBD’s 0.13″ microLED achieves 5,000 nits, enabling direct-view displays without waveguides—eliminating rainbow artifacts and expanding eye box to 15mm [14].
Pancake Lenses (Folded Optics):
Meta Quest 3 demonstrated 40% thickness reduction using polarized folded optics. Adapting this to smart glasses could shrink form factor to <20mm temple thickness.
Photonic Integrated Circuits (PIC):
Integrate laser sources, modulators, and waveguides on single chip—reducing optical engine size by 60% while improving efficiency.
Brain-Computer Interfaces (BCI):
Meta’s EMG (electromyography) wristband detects neural signals for gesture control. Future smart glasses may integrate dry-electrode EEG sensors for thought-based interfaces.
6G Connectivity (2030+):
Terahertz frequencies (100-300 GHz) promise 100Gbps+ throughput, enabling full holographic telepresence (1Tbps estimated requirement).
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What is the core technology behind smart glasses displays?
Smart glasses use micro-OLED or microLED displays combined with waveguide optics. The display engine projects images into transparent waveguides etched with nanoscale gratings, which redirect light toward the user’s eye through total internal reflection. This creates a see-through display overlaying digital content on the real world. Modern systems like Meta Orion achieve 70° field-of-view using silicon carbide waveguides with 2.6+ refractive index.
2. How do smart glasses process AI requests locally vs. in the cloud?
Smart glasses employ a hybrid AI architecture. Simple tasks like voice wake words, object detection, and gesture recognition run on the device’s NPU (Neural Processing Unit) for sub-100ms latency. Complex queries like conversational AI, real-time translation, and generative responses are offloaded to cloud servers via Wi-Fi/5G. For example, Qualcomm’s Snapdragon XR2 Gen 2 can run 7-billion parameter LLMs locally at 20 tokens/second, handling 80% of common interactions without cloud dependency.
3. What sensors do smart glasses use for spatial tracking?
Smart glasses integrate 9-axis IMUs (accelerometer, gyroscope, magnetometer) for head orientation tracking at 1000Hz sampling rates. Stereo cameras enable visual SLAM (Simultaneous Localization and Mapping) for 6DoF positional tracking with millimeter accuracy. Depth cameras (Time-of-Flight or structured light) measure distances for hand tracking and occlusion handling. Advanced models add GPS/GNSS for outdoor localization and UWB (Ultra-Wideband) for precise indoor positioning within 10-30cm accuracy.
4. How long do smart glasses batteries last and how are they charged?
Battery life ranges from 3-5 hours for continuous AR rendering to 8-12 hours for intermittent notifications. Ray-Ban Meta achieves 4-5 hours with its 800mAh battery, while lighter devices like Even Realities G1 last 8+ hours at 500mAh capacity. Most use pogo pin charging cases providing 3-4 additional full charges, delivering 15-20 hours total daily usage. Fast charging via USB-C PD achieves 0-80% in 45 minutes.
5. What operating systems do smart glasses run on?
Google’s Android XR (launched 2024) leads the open ecosystem, powering Samsung, XREAL, and Sony devices with native Gemini AI integration. Apple is developing visionOS Lite for rumored 2027 Apple Glass. Meta uses proprietary RTOS for Ray-Ban Meta, optimized for 3-second boot times and 50% lower power vs. Android. Enterprise models like RealWear Navigator run Android 11+ with XR extensions. All platforms support OpenXR 1.1 API for cross-platform app compatibility.
6. How do smart glasses connect to smartphones and other devices?
Bluetooth 5.3 provides the primary low-power link for notifications, voice commands, and sensor data, consuming <10mW in LE (Low Energy) mode. Wi-Fi 6E handles high-bandwidth tasks like firmware updates and cloud AI queries at up to 1.2Gbps. Some enterprise models integrate 5G Sub-6 modems for standalone operation, enabling telemedicine and remote assistance at 15Mbps uplink. Advanced pairing uses NFC for tap-to-connect setup, while UWB enables spatial awareness between devices for precise positioning.
Conclusion
Smart glasses technology in 2025 represents a mature convergence of cutting-edge display optics, powerful edge AI processing, and seamless cloud connectivity—packaged into all-day wearable form factors weighing under 100 grams. From silicon carbide waveguides enabling 70° fields-of-view to 12 TOPS NPUs running 7-billion parameter language models locally, today’s smart glasses deliver capabilities unimaginable during Google Glass’s 2013 debut.
The architectural blueprint reveals three critical technology pillars: hardware miniaturization (microLED displays, 4nm SoCs, 0.3mm vapor chambers), software intelligence (on-device LLMs, hybrid cloud AI, Android XR ecosystem), and connectivity infrastructure (Bluetooth 5.3, Wi-Fi 6E, 5G edge computing). Together, these enable transformative use cases—from enterprise workers achieving 25% faster inspections to consumers navigating cities with centimeter-accurate AR overlays.
Looking ahead to 2028, emerging technologies like direct-emission microLEDs, photonic integrated circuits, and 6G connectivity promise even slimmer form factors, longer battery life, and holographic displays. As AI smart glasses mature from novelty to necessity, understanding their underlying technology architecture becomes essential for developers, businesses, and consumers preparing for the post-smartphone era.
Ready to Integrate Smart Glasses Technology?
Contact us for OEM/ODM smart glasses technology solutions and custom AR hardware development
References
[1] SPIE. (2025). Getting Smart About Smart Glasses. Photonics Focus. https://www.spie.org/news/photonics-focus/julyaugust-2025/getting-smart-glasses
[2] Minimicroled. (2025). Micro LED For Waveguides: Full-Color AR Nears Production. https://www.minimicroled.com/micro-led-for-waveguides-full-color-ar-nears-mass-production/
[3] Meta. (2024). Introducing Orion: Our First True AR Glasses. Meta Connect 2024. https://about.fb.com/news/2024/09/introducing-orion-our-first-true-augmented-reality-glasses/
[4] Sony Semiconductor Solutions. (2025). ECX339A Micro-OLED Display Specifications. https://www.sony-semicon.com/en/products/microdisplay.html
[5] Meta. (2024). Quest Pro Technical Specifications. https://www.meta.com/quest/quest-pro/tech-specs/
[6] RealWear. (2025). Navigator 520 Technical Documentation. https://www.realwear.com/products/navigator-520
[7] Even Realities. (2025). How AI Glasses Work: The Complete Technology Guide. https://www.evenrealities.com/blog/how-ai-glasses-work
[8] IC Drex Electronics. (2024). Key Components Behind Smart Glasses Technology. https://www.icdrex.com/key-components-behind-smart-glasses-technology/
[9] Google. (2024). Android XR: Extended Reality Operating System. https://www.android.com/xr/
[10] Android Central. (2025). Android XR: Everything You Need to Know. https://www.androidcentral.com/gaming/virtual-reality/android-xr
[11] Vuzix Corporation. (2024). Enterprise Smart Glasses Case Studies. https://www.vuzix.com/pages/case-studies
[12] DHL. (2024). Smart Glasses in Logistics: Efficiency Report. DHL Supply Chain Innovation.
[13] Pew Research Center. (2024). Public Perceptions of Smart Glasses and Privacy. Technology & Social Trends Report.
[14] JBD. (2025). MicroLED Display Technology for AR/VR. https://www.jb-display.com/